- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- Re: Ask Me Anything - Configuration, Verification, and Troubleshooting of Dynamic Routing Protocols
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Ask Me Anything - Configuration, Verification, and Troubleshooting of Dynamic Routing Protocols
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-09-2019
02:56 PM
- last edited on
12-09-2019
03:12 PM
by
Hilda Arteaga
![]()
This topic is a chance to clarify your questions about the configuration, verification, troubleshooting and general best current practices of dynamic routing protocols. All questions regarding to general design, flooding, in-depth mechanics, and features of RIP, OSPF, IS-IS EIGRP, and BGP are welcome.
Dynamic routing protocols are a fundamental piece for internetworking, their main function is to provide the mechanisms to generate, process, and distribute topological and network layer reachability information (NLRI). Having an in-depth knowledge of routing protocols is key to understand modern overlay solutions such as Cisco DNA and a plethora of SDN designs, since these use some form of underlying routing form to perform connections under the hood.
To participate in this event, please use the ![]() button below to ask your questions
button below to ask your questions
Ask questions from Monday 09th to Friday 20th of December, 2019
 Elvin Arias is a devoted IP routing learner with a wide knowledge and experience in different technologies such as MPLS, x-EVPN, Segment Routing, IS-IS, MP-BGP, Network Programmability and Automation. He works as a Network Development Engineer in the Internet Edge Engineering team at Amazon in the EMEAR region, he focuses on Automation and R&S/SP technologies. Before that, he worked as a senior TAC engineer in the Service Provider team for the Americas theatre at Cisco. Elvin is an active member of the networking community where he often collaborates developing and publishing technical content or participating on live events or forum sessions for R&S and SP technologies for the Cisco Community, as well he engages in technical discussions in the Cisco Learning Networking community, where he has been honored with the Cisco Designated VIP distinction in multiple years 2013-2017. Elvin holds two CCIE certifications, one in R&s and one in SP (#57406)..
Elvin Arias is a devoted IP routing learner with a wide knowledge and experience in different technologies such as MPLS, x-EVPN, Segment Routing, IS-IS, MP-BGP, Network Programmability and Automation. He works as a Network Development Engineer in the Internet Edge Engineering team at Amazon in the EMEAR region, he focuses on Automation and R&S/SP technologies. Before that, he worked as a senior TAC engineer in the Service Provider team for the Americas theatre at Cisco. Elvin is an active member of the networking community where he often collaborates developing and publishing technical content or participating on live events or forum sessions for R&S and SP technologies for the Cisco Community, as well he engages in technical discussions in the Cisco Learning Networking community, where he has been honored with the Cisco Designated VIP distinction in multiple years 2013-2017. Elvin holds two CCIE certifications, one in R&s and one in SP (#57406)..
**Helpful votes Encourage Participation! **
Please be sure to rate the Answers to Questions
- Labels:
-
Other Routers
-
Routing Protocols
- AMA
- ask me anything
- ask the expert
- bgp
- ccie
- CCIE enterprise
- CCIE SP
- ccna
- CCNA R&S
- CCNA routing & switching
- CIE R&S
- cisco
- Cisco Community
- Cisco DNA
- cisco learning network
- Cisco VIP
- cln
- dynamic routing protocols
- eigrp
- Elvin Arias
- forum event
- ipv4
- ipv6
- is-is
- Layer 3
- lsas networking
- network layer reachability information
- next hop
- nlri
- ospf
- rip
- routing protocols
- routing tables
- sdn
- troubleshooting vector distance
- verification virtual link
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-19-2019 01:34 PM
In a DMVPN network i have several static routes. I've redistributed those routes into EIGRP. However I noticed there are several static routes that point to public IP address. How do I redistribute the static routes but leave out the static routes pointing to the public IP address in EIGRP? Do i use a route-map with an access-list permitting only the networks that i need redistributed? Or is there another way to do this?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-20-2019 01:09 PM
From an administration standpoint, is better to use a prefix-list + route-map combination. You would do it like this:
1. Static routes
ip route 8.8.8.8 255.255.255.255 Null0 name PUBLIC_SPACE
ip route 8.8.8.9 255.255.255.255 Null0 name PUBLIC_SPACE
ip route 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 Null0 name PRIVATE_SPACE
ip route 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.255 Null0 name PRIVATE_SPACE
!
2. Create matching IP prefix-list (permitting) matching the prefixes you want to redistribute
ip prefix-list PRIVATE_ONLY seq 5 permit 192.168.1.1/32
ip prefix-list PRIVATE_ONLY seq 10 permit 192.168.1.2/32
3. Create route-map matching the prefix-list and deny the routes
route-map PRIVATE_ONLY permit 10
match ip address prefix-list PRIVATE_ONLY
!
route-map PRIVATE_ONLY deny 20
!
4. Attach it to the IGP
router eigrp 100
redistribute static route-map PRIVATE_ONLY
/End.
Elvin
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-21-2019 04:59 AM
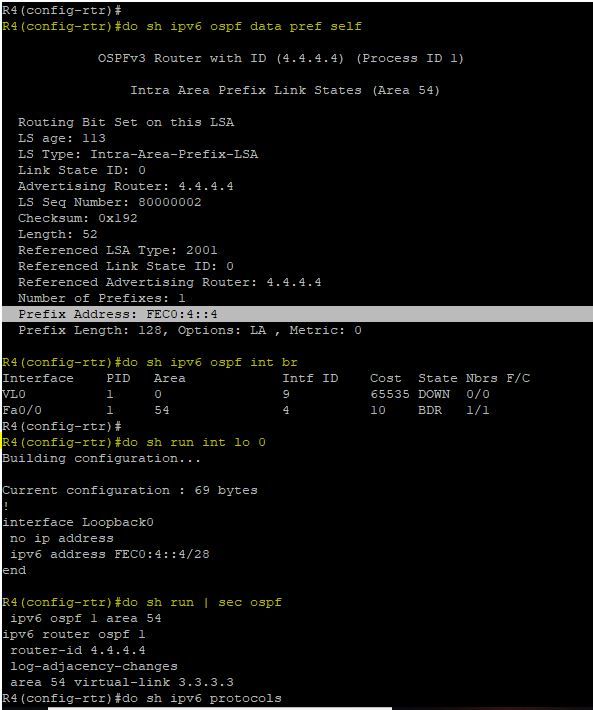
Hello @Elvin Arias
I have not enabled OSPF on the loopback interface, but still, I can see the prefix in the type 9 LSA.
This was not happening when I remove the virtual-link command, so what is the relation?
Please refer below pic
Thanks
Siva
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-23-2019 07:39 PM - edited 12-24-2019 05:35 AM
Hi Siva,
This is the expected behavior and it has to do with how virtual-links operate in OSPFv3.
Remember that operations for OSPFv3 at a link level are performed using the IPv6 Link Local address range FE80::/10, but one inherit quality of using these addresses is that packets originated with link local address as destination cannot be processed outside the local link.
This works fine on adjacencies with directly connected neighbors, but virtual-links do not belong to this category, virtual-links form special multihop adjacencies and OSPFv3 packets must be encapsulated with routable IPv6 Global Unicast addresses, otherwise packets will not be able to exit the local segment and there won't guarantee that the virtual-link will be established.
When no routable addresses are being advertised in the area, OSPFv3 will automatically solve this by advertising one IPv6 Global Unicast address. RFC 5340 states that:
"...If RTX has one or more virtual links configured through the area, it includes one of its global scope IPv6 interface addresses in the LSA (if it hasn't already), setting the LA-bit in the PrefixOptions field, the PrefixLength to 128, and the Metric to 0. This information will be used later in the routing calculation so that the two ends of the virtual link can discover each other's IPv6 addresses."
This is the reason why a type-9 LSA was "magically" generated on your case. ; )
Elvin
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-24-2019 07:20 AM
Good explanation, Thanks for the reply.
Is there any order for this prefix preference? like if I have both physical and loopback interfaces with Global unicast IPv6 address assigned, which one will be used for the virtual link?
and if I have enabled OSPFv3 on both the interfaces which one will be used as a virtual link source?
One more question,
could you please tell me how the Interface ID ("Interface ID 9") number is calculated in ospfv3.
Thanks
Siva
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-28-2019 08:31 AM - edited 12-28-2019 08:52 AM
Hi Siva,
Sorry for the delay, holiday season :)
1. OSPFv3 does not mandate vendors as to what algorithm to use to implement the Interface ID, it suggest the use of SNMP MIB-IfIndex to match with the Interface ID, but this is up to the implementation. You can refer to section 4.1.2 of RFC 5340 for the advisability on this.
The actual Cisco's implementation is based on an internal index of the interface as the Interface ID. There is a process that holds and manages the interfaces internally in XE, it is called the Interface Descriptor Block (IDB). All interface media types are sorted/indexed on this database.
Note: IOS-XR also has similar concept, called Micro Interface Descriptor Block (UIDB).
If we take an OSPFv3-enabled router as an example, we will see the numbering matching.
.OSPFv3 Interface ID:
IOU4#show ospfv3 interface | include Ethernet|Loopback|Interface ID Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up Link Local Address FE80::A8BB:CCFF:FE00:400, Interface ID 19 Loopback interface is treated as a stub Host Ethernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Link Local Address FE80::A8BB:CCFF:FE00:400, Interface ID 2
.Interface Descriptor Block (IDB):
IOU4#show idb | include Ethernet0/0|Loopback0 H 1 2 U,A,R Ethernet0/0 (HW SB CDP(5), HW SB LLDP(3), Ether(1)) H 17 19 U,R,R Loopback0 (Ethernet Infra and Switchport PCB(6)) S 1 2 U Ethernet0/0 (Ether-OAM(17), ONEP interface subblock(16), IPv6 Routing(15), SW OSPFv3(14), SW IPV6 STATS FORWARDING(13), SW IPV6 ICMP(11), IPv6(10002), IPv6 Interface SB(10), SW CDP(9), MPLS FEATURE(8), NetBIOS(6), SWSB IPROUTING(4), SW SB LLDP(2), KEEPALIVE(1)) S 17 19 U Loopback0 (IPv6 Routing(15), SW OSPFv3(14), ONEP interface subblock(16), NetBIOS(6), SW IPV6 STATS FORWARDING(13), SW IPV6 ICMP(11), IPv6(10002), IPv6 Interface SB(10), SWSB IPROUTING(4), MPLS FEATURE(8), KEEPALIVE(1))
As observed, Index number correctly matches. Also note that in recent XE versions, the SNMP MIB-ifindex numbering schema is used, for consistency purposes. If on your version this is not the case, you could optionally enabled it by issuing the OSPFv3 global router command:
router ospfv3 1 interface-id snmp-if-index
With this, SNMP interface index will be used for OSPFv3 Interface ID.
/
2. Regarding the address selection, it should be according RFC6724. More details here, https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6724.
Happy holidays,
Elvin
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-28-2019 06:42 PM
Thank you very much for the information
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-28-2019 07:20 PM
Elvin
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-02-2020 10:45 AM
Where can I find setup examples for SSL/IPSEC, PPTP and L2TP VPN configuration for the RV34X series routers? Minimal site documentation (all tried w/o success), manual is not helpful...have not Googled successfully....logged errors are minimal and unhelpful.
I get pop ups saying router misconfiguration and authentication failure though all seems to be set up correctly...I DO connect.
Do I NEED an internal DNS server?
Do I need to set up strict password verification?
Do I need to have a different subnet range for each methodology (eg 192.168.3.1-30 for PPTP, 192.168.4.1-30 for SSL/IPSEC, 192.168.5.1-30 for L2TP)?
Tried connecting with Fortinet VPN client on Mac and Win and with internal connection apps on current Mac and Win10.
You said 'ask me anything...' ;-)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-03-2020 05:31 AM
I am not familiar with this router and the GUI associated with it, but configuration examples can be found here (link below) for different features, I checked and was able to see VPN and L2TP tech notes.
Sorry for the delay, the event is closed now, but I'm glad to answer! :)
Elvin
- « Previous
-
- 1
- 2
- Next »
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide