- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Security Knowledge Base
- ASA NAT 8.3+ - NAT Operation and Configuration Format (CLI)
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-20-2013 12:55 PM - edited 03-08-2019 06:48 PM
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Version History
- Possible Future Updates
- Documents Purpose
- NAT Operation in ASA 8.3+
- NAT Configuration Structure and Considerations
- The Format and Elements of NAT Configurations
- Objects / Object-groups
- Naming Objects
- Network Object NAT
- Static NAT & Static PAT
- Dynamic PAT & Dynamic NAT & Dynamic NAT+PAT
- Twice NAT / Manual NAT
- Dynamic PAT & Dynamic NAT & Dynamic NAT+PAT
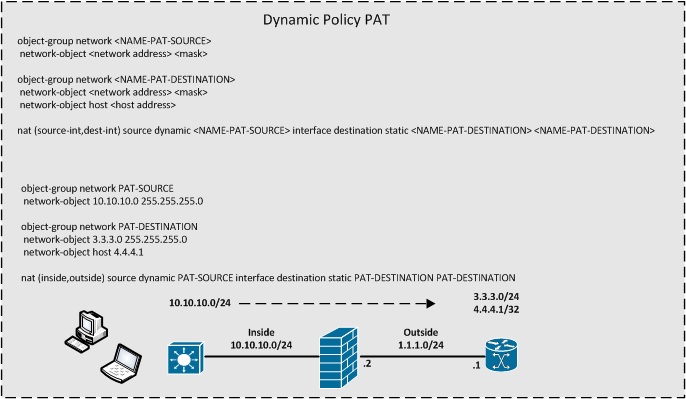
- Dynamic Policy PAT
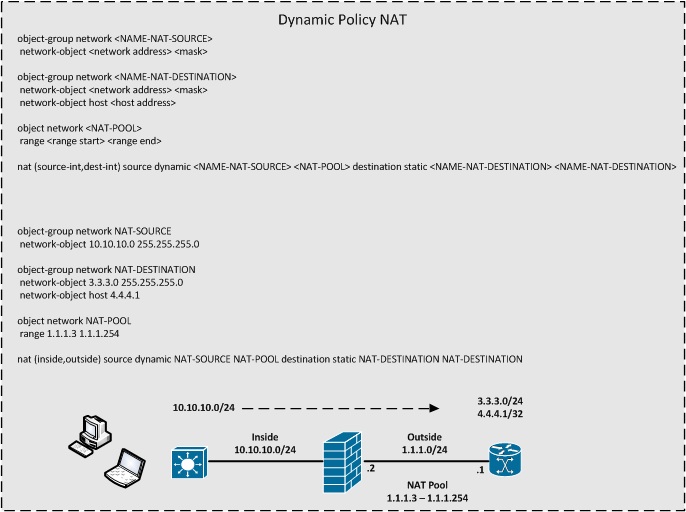
- Dynamic Policy NAT
- Dynamic Policy NAT+PAT
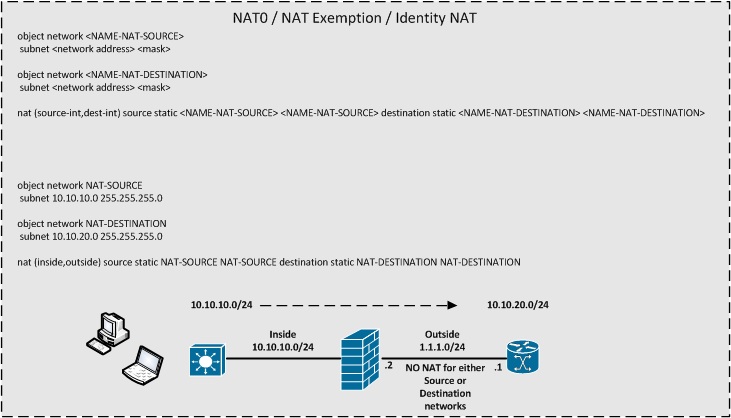
- NAT0 / NAT Exemption / Identity NAT
- Static Policy NAT
- Static Policy PAT
- How to Utilize the NAT Sectioning
- Public IP Address Considerations
- The Format and Elements of NAT Configurations
- Supporting Documentation
- Final Word
Introduction
My name is Jouni Forss. I have worked in Finland at a local ISP for 5 years as a networking Engineer in a unit dedicated to servicing business customers. My work for the most part consists of managing/installing/developing Firewall and VPN environments that include the use of Cisco PIXs , FWSMs and ASAs.
I participate at the Cisco Support Community in the Firewall and VPN section. And of those mainly at the Firewall section.
Version History
- 20.3.2013 Initial version
- 22.3.2013
- Added Pictures attachement
- Added NAT Configurations Text Files attachment
Possible Future Updates
The Initial version of this document is supposed to provide some basic information on the new 8.3+ NAT format. I will possibly add some more sections to the document but the main point initially was to get some version of this document out. If you want to get a notifications on the changes to this document you can check the setting from the right side panel of this page while logged in to the CSC.
Documents Purpose
This documents purpose will be to act as an informative document for users new to ASA NAT configurations in general or just the New ASA NAT 8.3+ configurations format. The content directly reflects the things I run into my day to day work or things that get asked on the CSC (Cisco Support Community) Firewall and VPN sections.
The document naturally wont contain every possible setup regarding the NAT but more might be added later. Suggestions are welcome.
NAT Operation in ASA 8.3+
Sections
The new NAT format in 8.3 (and newer) software has introduced changes to how the NAT rules are ordered in the ASA configurations. NAT configurations are now divided into 3 different sections. The Section determines the order of the NAT rules matched. Section 1 NAT configurations are gone through first then Section 2 and finally Section 3
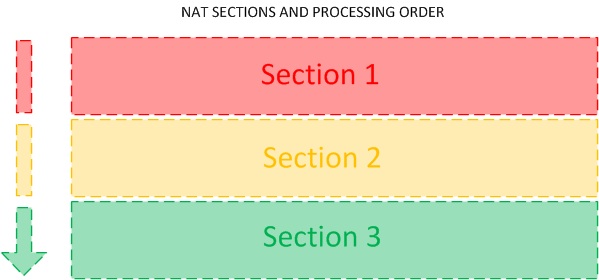
Rule Types
There are 2 NAT Rule Types
- Twice NAT / Manual NAT
- Network Object NAT
The NAT Rule Types refer more to the configuration format of the NAT than the actual type of the NAT (Dynamic PAT, Static PAT and so on). Below is more information on both of the NAT Rule Types
Network Object NAT
Network Object NAT always consists of a "object network <object name>" configuration which holds a configuration for host address/subnet/range and binds that to a NAT rule also present inside that same "object network". In other words all configuration related to the NAT configuration are gathered under a single "object network".
Notice that this is totally different than "object-group network <object-group name>". NAT configurations CANT BE configured under "object-group network"
This "object network <object name>" can be later referenced in other configurations with the name of the object. (ACL configurations)
Twice NAT / Manual NAT
Twice NAT / Manual NAT is not configured under any "object network" or "object-group network".
Instead Twice NAT / Manual NAT uses both "object network" and "object-group network" as its configuration parameter to define the source and destination addresses/subnets/networks/ranges for your NAT configurations.
Twice NAT / Manual NAT also lets you utilize "object service <object name>" to manipulate the source and destination TCP/UDP ports in the NAT configurations.
The key thing with Twice NAT / Manual NAT compared to Object Network NAT is that you can manipulate both address/port source and destination paremeters of the NAT. Therefore Twice NAT / Manual NAT gives you alot more options than Network Object NAT.
Rule Types used per Section
The mentioned 3 Sections use different NAT Rule Types.
- Section 1 uses Twice NAT / Manual NAT
- Section 2 uses Network Object NAT
- Section 3 uses Twice NAT / Manual NAT
Twice NAT are by default inserted to the Section 1 of NAT rules on the ASA so they are the first ones matched against traffic incoming to the ASA. Network Object NAT rules are always inserted to the Section 2 of NAT rules. Twice NAT rules configured with an "after-auto" parameter will be moved to Section 3 of the NAT configuration and will therefore be the last NAT rules matched on the ASA firewall.
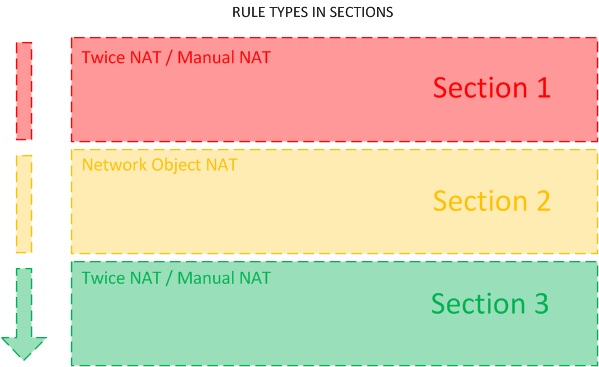
NAT Types used with Twice NAT / Manual NAT and Network Object NAT
So far we know that NAT operates in 3 Sections and that each Section uses only certain Rule Type.
Now we can have a look at which NAT Types are usually configure with each NAT Rule Type. Take note that the below mentioned NAT Types per each NAT Rule Type and the related commens inside "()" arent the absolute truth on how you are supposed to configure NAT. It all depends on your networks complexity among other things.
NAT Types of Network Object NAT (but NOT LIMITED to)
- Static NAT
- Static PAT (= Port Forward)
- Dynamic Normal PAT (Usually done as Twice NAT in Section 3 instead of Section 2)
- Dynamic Normal NAT (Usually done as Twice NAT in Section 3 instead of Section 2)
- Dynamic Normal NAT+PAT (Usually done as Twice NAT in Section 3 instead of Section 2)
NAT Types of Twice NAT / Manual NAT (But NOT LIMITED to)
- Dynamic Normal PAT (Used in Section 3)
- Dynamic Normal NAT (Used in Section 3)
- Dynamic Normal NAT+PAT (Used in Section 3)
- Dynamic Policy PAT (Used in Section 1, possibly Section 3)
- Dynamic Policy NAT (Used in Section 1, possibly Section 3)
- Dynamic Policy NAT+PAT (Used in Section 1, possibly Section 3)
- NAT0 / NAT Exemption / Identity NAT (Used in Section 1)
- Static Policy NAT (Used in Section 1)
- Static Policy PAT (Used in Section 1)
What you have to notice regarding the Twice NAT / Manual NAT is the fact that IT CAN BE USED IN BOTH SECTION 1 and SECTION 3. Part of the mentioned NAT Types are therefore usually only used in Section 1 and others only used in Section 3.
No use using a NAT0/Identity NAT configuration in Section 3 when every other NAT rule will possibly override it because of the order the NAT is processed.

Ordering of Rules Types Inside Sections
So as mentioned in this document already, the Sections of the NAT configurations already lay a foundation on what the Order/Priority of the NAT configurations should be. In addtion to this each section has a certain ordering of NAT rules.
Section 1 and Section 3 (Twice NAT / Manual NAT)
Twice NAT / Manual NAT has its own "line" parameter value that you use with the command.
It operates/behaves the same way as ACL "line x" configurations in that it moves the existing (on the line used) and any rule after it one line number down wihtout removing any existing NAT configuration. Naturally there is a chance that the configured rule will override some later rule because it was inserted inbetween the existing configuration.
Opposed to 8.2 (and below) software levels, this gives you the chance to insert a NAT rule where want without the need to remove the existing NAT configurations (Compare 8.2 Static NAT vs. Static Policy NAT between same interfaces for example. If Static NAT has been configured first it will always override the Static Policy NAT for the same interfaces)
Section 2 (Network Object NAT)
Network Object NAT behaves more like the older 8.2 (and below) software. It has a set order by which it decides what NAT rule to use. You cant manipulate the order of the NAT rules with any kind of "line" value. The only way to control the Section 2 Network Object NAT order is based on how specific the NAT rules parameters are.
The Section 2 NAT however does have line number visible in some of the command output BUT this value is determined by the ASA and as soon as you enter a new Object Network NAT configuration the ASA calculates the new order of the Network Object NAT rules.
Below is more on what factors into the priority of which Object Network NAT rule is used.
The first deciding factor in order is the NAT Type
- Static
- Dynamic
Inside the above mentioned NAT Types the following order applies
- Amount of IP addresses contained in "object network"
- For "object network" containing same amount of IP addresses the lowest IP address number is first in order
- For "object network" being equal on both above counts will be ordered by the alphabetical order of their names

NAT Configuration Structure and Considerations
The Elements and Format of NAT Configurations
This sections purpose is to go a bit more into the actual format and elements of the new NAT configurations.
From the 8.2 (and older) NAT format we remember that that the three commands ("global", "nat" and "static") that form the basis of the NAT configurations. Generally you would only use IP addresses or networks as the parameters of the NAT configuration. In special cases you would use "access-list" configurations to either define a NAT0 or Policy NAT configuration.
In the software 8.3 (and newer) there are no more ACLs in NAT configurations. You also very rarely refer to an actual IP address or network directly in the NAT configuration line. The new NAT format now utilizes "object network" , "object service" and "object-group network" to define the parameters of the NAT configuration. Naturally also the source and destination interface "nameif" and the keyword "interface" will play a role.
Objects / Object-groups
As mentioned above (and earlier in the document), the NAT configurations now rely heavily on "object" and "object-group" configuration to provide the information to the actual NAT configuration.
You will be using the following as a parameter of Twice NAT / Manual NAT configurations
- object-group network <NAME>
- Used to define multiple networks, host addresses or combination of both in NAT configurations
- object network <NAME>
- Used to define a single subnet, address range or host address in NAT configurations
- object service <NAME>
- Used to define source/destination services in NAT configurations
You can use the following as a parameter of Network Object NAT
- object-group network <NAME>
- Used to define multiple networks, host addresses or combination of both in NAT configurations
- object network <NAME>
- Used to define a single subnet, address range or host address in NAT configurations
And I say you "CAN" use the "object" and "object-group network" even under a Object Network NAT but to this day I have still not done this. The situation where you might do this is when you configure a Dynamic NAT/PAT/NAT+PAT configuration as an Network Object NAT.
Naming Objects
Naming the "object" and "object-group" objects in your configuration will play a big part in your NAT configurations. As almost every single one of your NAT rules will rely on some sort of object its good to come up with a policy for naming objects that will remain logical. It will save you time and possibly help in troubleshooting situations also.
My personal preference is to use CAPS configuring the "object" or "object-group" name. The most important reason for this is the fact that almost every command on the ASA uses lower case letters. In a NAT configuration using CAPS means that you can read the CLI format configuration more easily as the used "object" and "object-group" names stand out better from the configurations.
The ASA does give you some options to rename objects/ACLs in the configuration though sadly this doesnt apply to every object type used in the NAT configurations.
You can rename
- object network
- object service
- access-list
With commands
- object network <name> rename <newname>
- object service <name> rename <newname>
- access-list <name> rename <newname>
You CANT rename
- object-group
Network Object NAT
This section will list the basic configuration format for the Network Object NAT
Static NAT & Static PAT

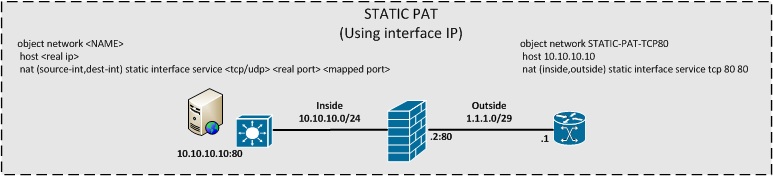

Dynamic PAT & Dynamic NAT & Dynamic NAT+PAT
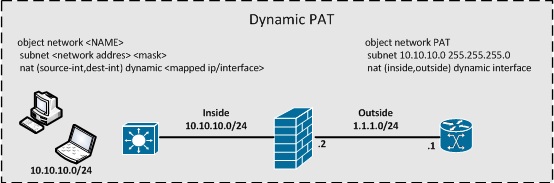
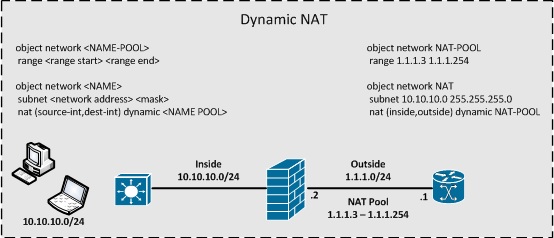

Twice NAT / Manual NAT
This section will list the basic configuration format for the Twice NAT / Manual NAT
Dynamic PAT & Dynamic NAT & Dynamic NAT+PAT
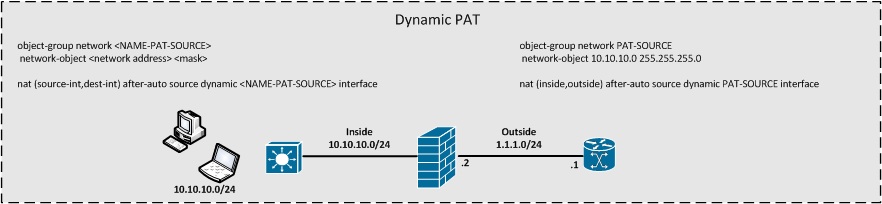
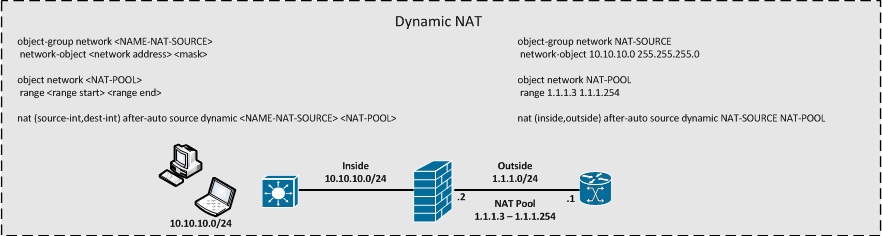
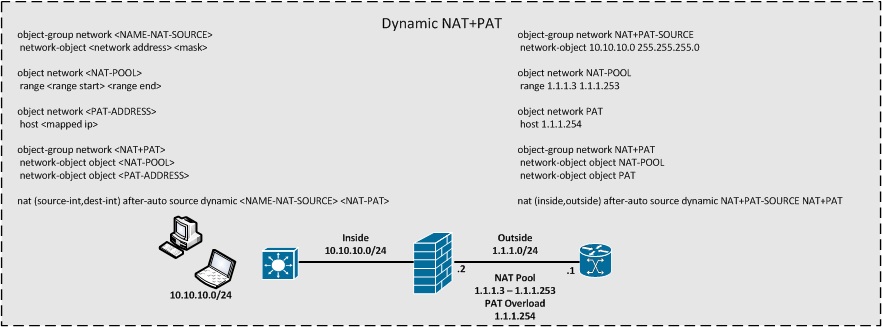
Dynamic Policy PAT
Dynamic Policy NAT
Dynamic Policy NAT+PAT

NAT0 / NAT Exemption / Indentity NAT
Static Policy NAT

Static Policy PAT

How to Utilize the NAT Sectioning
So far in this document we have discussed how the NAT configurations are structured in the new 8.3+ software levels.
We have seen that there is 3 Sections are processed in order
- Section 1
- Section 2
- Section 3
We have seen that there is a Rule Type for each section
- Section 1 - Twice NAT / Manual NAT
- Section 2 - Network Object NAT
- Section 3 - Twice NAT / Manual NAT
We have seen what NAT Types can be configured with each NAT Rule Type.
The next question would be how to organize all this information so configuring NAT on the ASA would be as clear as possible. I personally configure NAT rules so that each Section serves a specific purpose and/or specific users
Section 3 - The Default Dynamic Rules for Networks
The NAT configurations located in Section 3 are the last ones to be matched against a packet coming through the ASA. It seems only fitting to me that this should be the Section where you build your most basic NAT rules. Here you build the Dynamic PAT or Dynamic NAT or Dynamic NAT+PAT for all the users so that they will have some "last resort" NAT when they are connecting to networks past the ASA firewall.
As Section 3 holds Twice NAT / Manual NAT type configurations you also have the possibility to create destination based NAT rules so I would also possibly consider creating Dynamic Policy PAT / NAT / NAT+PAT rules for the users here.
In this case you will have to make sure that you order the rules under the Section correctly. This basically means that you should insert the Dynamic Policy PAT / NAT / NAT+PAT rules for a certain pair of source/destination interfaces before the the Default Dynamic PAT / NAT / NAT+PAT rule so it wont override the Policy rule inside the same section.
Section 2 - The Default Static Rules for Single Hosts
The NAT configurations located in Section 2 are matched against packet coming through the ASA before the Section 3 rules. This makes it a natural place to configure host specific NAT rules that you dont want to fall into the Default NAT Rules.
As Section 2 holds Network Object NAT rules, you dont have as much possibilities as with Twice NAT / Manual NAT. For the most common Static NAT and Static PAT configurations the Network Object NAT of Section 2 is more than enough to meet the basic requirements for hosting services
Section 1 - The Special Dynamic/Static NAT Rules for Networks and Single Hosts
The NAT configurations located in Section 1 are matched against packet coming through the ASA before any of the other Sections. This makes Section 1 the place where you will want to configure some rule that needs to override any other rules you might have for the same hosts/servers/networks. Naturally at the same time you will have to be extra carefull in what you really define here because there is obviously the highest risk of overriding something that you were not supposed to override.
As Section 1 holds Twice NAT / Manual NAT rules you manipulate both source and destination parameters of the NAT. Section 1 would therefore be the section to use for example for NAT0 / NAT Exempt / Identity NAT type configurations different Dynamic/Static Policy NAT/PAT configurations.
Sections Combined
When we combine the above defined roles of the different Sections we get the following general view of what NAT configurations we should use in each Section. Again, this is what I am used to doing and doesnt mean this wouldnt work in some other way.
- Section 1
- NAT0 / NAT Exemption
- Policy PAT / NAT / NAT+PAT (for everything when Section 2 host based rules need to be overridden also)
- Non-standard NAT configurations
- Section 2
- Static NAT
- Static PAT (Port Forward)
- Section 3
- Default PAT / NAT / NAT+PAT
- Policy PAT / NAT / NAT+PAT (for users)
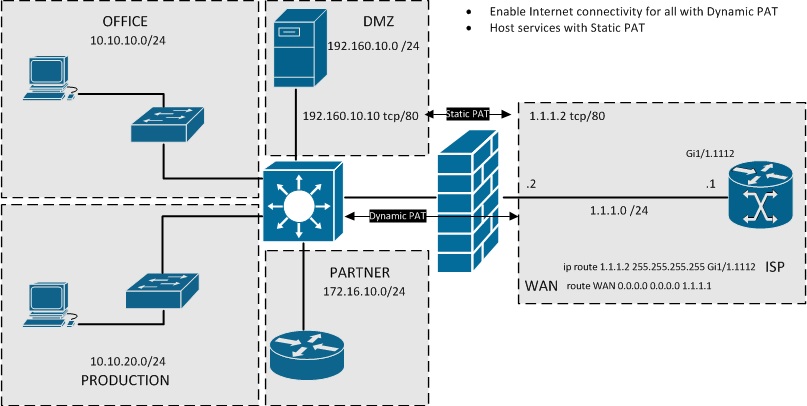
Public IP Address Considerations
This sections purpose is simply to suggest some things to consider regarding the use of the public IP addresses you are given by the local ISP. Wether they will help you naturally depends largely on how your ISP functions and what it provides.
Single IP Address
- Use Bridged WAN connection to the ASA when possible
- Use Static Public IP address if possible
- Ask for the possibility of MAC address binded DHCP if a Static Public IP address isnt possible otherwise
- If forced to use DHCP consider using Dynamic DNS
- Provide Internet access with Dynamic PAT and host local services with Static PAT
Probably the most common situation for any smaller company.
If possible, try to get a bridged device to provide the Internet connectivity to enable you to use the ISP provided public IP address straight on your ASA. This will make related NAT configuration easier and avoid the complexity and potential problems having a router in front of ASA also doing NAT.
If you are planning on hosting any services on a local server or using the ASA as a endpoint for VPN connection, try to get a static public IP address from the ISP. If a Static Public IP address isnt possible, consider asking for the possiblity of binding a DHCP address to your devices MAC address
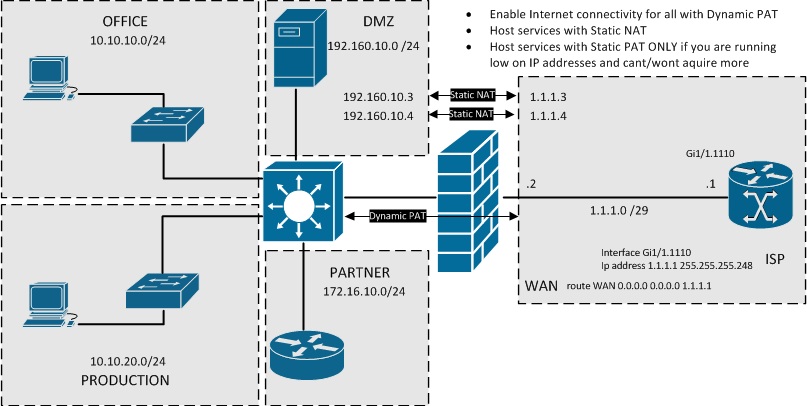
Small Subnet
Also a pretty common setup. Usually a /29 (or 255.255.255.248) public subnet provided to you by the ISP. Remember that 3 of the 8 IP-addresses provided by the /29 sized subnet are already taken from the start for other purposes and you will have 5 IP address at your disposal.
For example
- Network 1.1.1.0/29
- 1.1.1.0 = Network Address
- 1.1.1.1 = Gateway (can naturally be some other IP address from the subnet)
- 1.1.1.7 = Broadcast Address
- 1.1.1.2 - 1.1.1.6 = Usable Addresses on your ASA (one for ASA interface)
The probably most common setup would be to use one public IP address as the ASA "outside" interface IP address and also as the PAT IP address for all outbound traffic from your LANs or DMZs. Other IP addresses could be reserved for Static NAT use of servers. You should only resort to Port Forward / Static PAT configurations if you know you wont have public IP addresses for all your server needs.
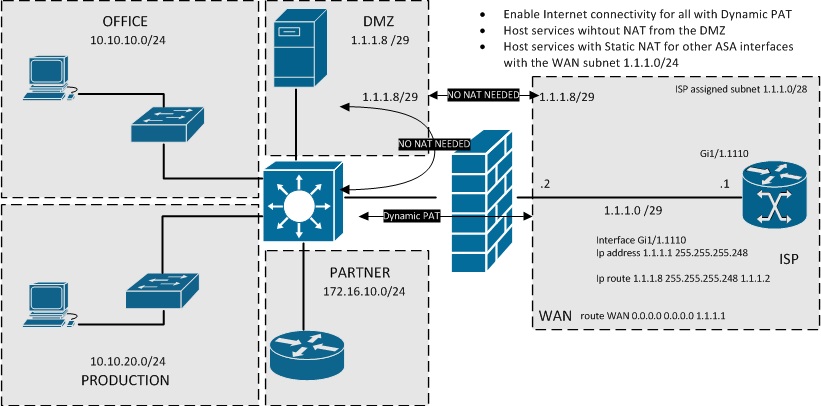
Large Subnet
I guess this is a relative term. I would already consider a /28 (255.255.255.240) or /27 (255.255.255.224) network a Large public Network in our cases. Personally I dont see many bigger networks/subnets handed out to business customers anymore. Only the bigger ones usually have 1 - 3 /24 subnets.
When assigned with a /28, /27 or bigger network I would already consider splitting the networks into 2 to be used for different purposes and in 2 different places in your network.
For example using one subnet for the link between you and the ISP which can be utilized for Default PAT configurations and possibly Static NAT configurations for server other than the ones hosted on the DMZ of the ASA. Other segment could be used direcly on the ASA DMZ interface or further on in your network on some other L3 device which provides the gateway for the servers.
Though naturally by segmenting an already relatively small subnet (even though I call them large in this situation) means you are wasting some public IP addresses as they will be deemed as network/gateway/broadcast address.
The idea/reason with segmenting the public subnets is that you can have the actual servers with the public IP addresses without the need to resort to any special NAT setups on the ASA side. You also can avoid problems related to DNS, especially when you have a DNS server local to the users LAN.
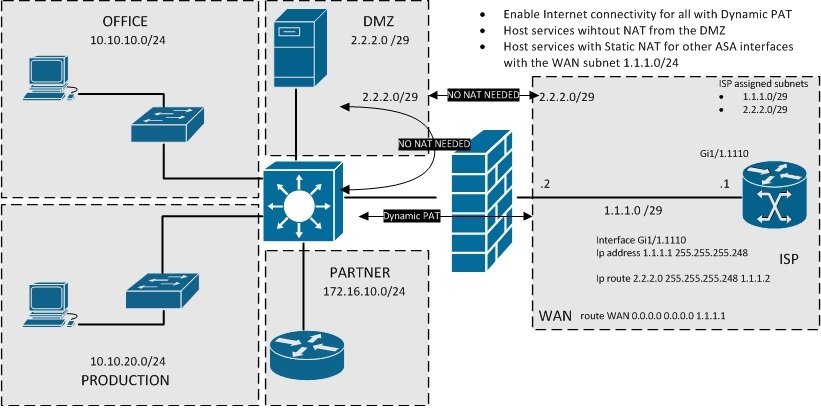
Multiple Subnets
With multiple discontinuous public subnets at our disposal I would also suggest considering the same option as above. Using a subnet directly on the DMZ segments to avoid any special needs regarding the NAT and DNS while at the sametime using other subnet(s) directly on the ASA firewall "outside" facing the ISP
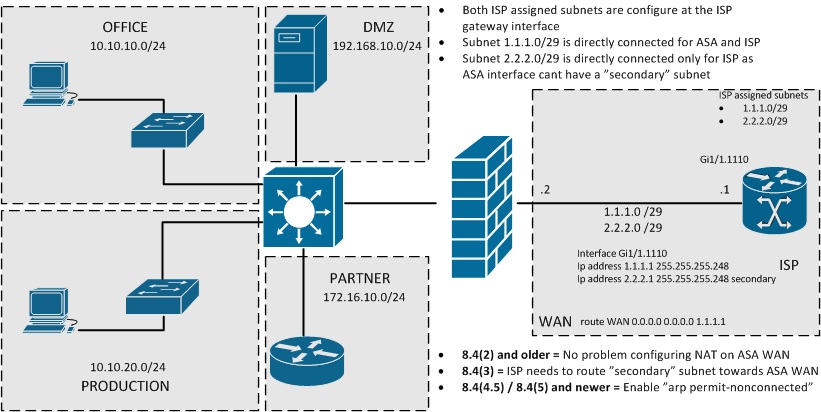
One thing to keep in mind with using multiple subnets on the interface facing the ISP is that there have been changes from software version 8.4(2) -> 8.4(3) -> 8.4(4/5) in how the ASA operates with multiple subnets on one interface. This mostly depends on how the ISP has handled the routing of your public subnets.
If the ISP has for example configure a new public subnet as a "secondary" network on their gateway interface AND you are using 8.4(3) software you will run into problems with connectivity of the hosts in the "secondary" network range. This is because of changes to ARP related behaviour. Basically the ASA will not populate ARP table with nonconnected networks.
Your solution is either to ask the ISP to route the new subnet directly towards the ASA "outside" interface IP address OR you will have to upgrade the ASA to 8.4(4/5) software level and use the configuration command "arp permit-nonconnected"
Supporting Documentation
Cisco ASA Gonfiguration Guides
- Contains example configurations
- Provides background information/theory
- Provides information about possible limitations
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6120/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
Cisco ASA Command References
- Contains more detailed information on different ASA configuration commands
- Gives usage guidelines
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6120/prod_command_reference_list.html
Cisco Support Community Firewall Discussion Area
- Ask questions related to NAT from both Cisco Employees and Experts
https://supportforums.cisco.com/community/netpro/security/firewall?view=discussions
Final Word
Hopefully you have gotten some new information from this document and it has helped you someway. If you have found it helpfull please do take the time to rate it.
Suggestion about possible additions to the document are welcome. Please keep specific question about how to configure some NAT configurations to the actual Firewall section of CSC (link provided just above) If you happen to find some error in the document that I have missed please let me know and I will try to correct it.
- Jouni
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
just WOW! that was great ;)
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Jouni,
Thanks for the info. But i would like to which the best for this scenario for allowing specific address on nat while any other address are not allowed.
thanks
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Excellent Document
Thank you very much !!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I go through this document more often to refresh my ASA NAT knowledge. I must appreciate efforts put by Juoni. Thank you very much.
I have one query though-
If I have 2 twice NAT statements
1. Static PAT (For port forwarding)
2. Identity NAT (For site-to-site VPN tunnel)
Considering execution of section 1 NAT rules, Traffic from internal server for which I have added 1st NAT rule, wont be able to pass through the tunnel because of rule 1 getting executed always.
Correct me If i am wrong?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thank you very much for this valued document. it helps me alot on day to day jobs on firewall natting.
thank you very much.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Excellent document, Thank you very much!!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thank you very much!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello Jouni Forss,
Your document is excellent,. an i need one help, a planning to change my designation form Network to Firewall, am studying some basic things,
Rite now am working in ASA 5505 firewall,
I want to know from you,
1. what are the things want to study about firewall
2. If i will go to interview, what kind of question they will ask
3. how to configure and work site to site VPN.
Please guide me, and give your number if any dought i will call and clear that.
Thank you.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
Thanks for this!
What is the order of operation then if the traffic is from a lower security level to a higher security level?
Example:
lower security interface > higher security interface
1.acl
2.twice nat
3.route
source IP (unchanged) > destination IP (translated or changed)
Would the return traffic need also an ACL allowing
higher security interface > lower security interface
source IP (translated) > source IP (changed back to mapped IP) destination IP
If you need further details, please just ask.
Cheers,
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The inbound-acl applied to lower-security interface will reference the real destination-IP not the mapped-IP.
So the order: NAT(untranslate), consult acl and if allowed, route to real-destination.
Return traffic doesn't need to be explicitly allowed via a separate inbound-acl on higher security interface.
Pre-8.3 implementations needed the mapped-destination-IP
Order: consult acl and if mapped-destination-IP is allowed, untranslate to real-dest-IP and route.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
First of all, I want to thank Jouni Forss for posting such useful document. I came across it due I was looking for HOW TO APPLY ACLs to NAT/PAT on ASA. I am quite familiar with IOS, so I was thinking that it would be like in IOS. I mean, in IOS NAT/PAT is defined by ACLs. I am wondering, is there more option than applying ACLs to the interfaces for packet filtering for NAT/PAT on ASA?
Cheers.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
I need to do NAT source & destination at the same time i.e Which means when a packets goes frm inside to outside, source changes to 10.4.2.2/32-this is the WAN IP (for source ANY) and destination changes to 192.168.1.0/24 (for destination matching 172.17.0.x/24) and vice versa.
Which diagram should i refer to? Sorry i m beginner.
- « Previous
- Next »
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community:




