- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Security Knowledge Base
- ISE BYOD Flow Using Entra ID
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
05-10-2021 10:02 PM - edited 07-28-2025 03:07 PM
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Requirements
- Components Used
- Assumptions
- Configuration
- SAML IdP Configuration
- ISE Policy Elements and BYOD Portal
- Entra ID SAML SSO Configuration
- Complete the SAML Configuration in ISE
- Complete the ISE Policy Configuration
- Configure the Wireless LAN Controller
- Verify the configuration
Introduction
*** NOTE: Microsoft has now renamed Azure AD to Entra ID. For all references to Azure AD in this document, the same concepts apply to Entra ID.
With the enhancements in ISE 3.0 for integrating with Entra ID via SAML IdP, it is now possible to create a BYOD Flow to provide Wireless network access using an employee’s Entra ID credentials.
The use of Entra ID credentials is an alternative to using a certificate-based method such as EAP-TLS (which requires certificate provisioning) or PEAP-MSCHAPv2. It can mitigate concerns with using other password-based authentication methods (like PEAP-MSCHAPv2) as it uses the employee’s email address as the username rather than exposing their on-premise Active Directory attributes such as sAMAccountName.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Cisco ISE 3.0
- Basic knowledge about SAML SSO deployments
- Entra ID
Components Used
This configuration example is based on the following environment:
- ISE 3.0 patch 2
- AireOS-based Wireless LAN Controller (2500, 5500, etc) with software version 8.5 or higher
- A separate Wireless SSID using Open authentication
- Basic open internet access for employees
- Entra ID user accounts associated with a BYOD Security Group
The following diagram illustrates the logical flow for the solution.
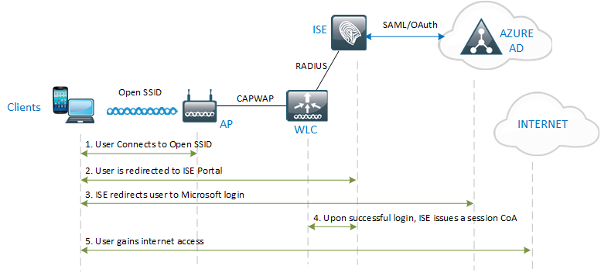
The lab used to validate the solution uses a single WLC, but the same solution will also work with a Foreign & Guest Anchor architecture.
Assumptions
The configuration herein assumes that an SSID has been created on the WLC for the BYOD network and the WLC has already been configured as a Network Device in ISE.
See the AireOS WLC configuration for ISE document for Open SSID WLAN configuration and best practices.
Configuration
SAML IdP Configuration
Step 1 – Create a new SAML Identity Provider for Entra ID
Navigate to Administration > Identity Management > External Identity Sources > SAML Id Providers and click Add.
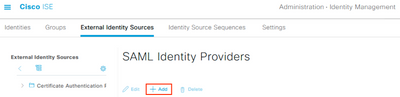
Input the Provider Id Name and optional Description values and click Submit.
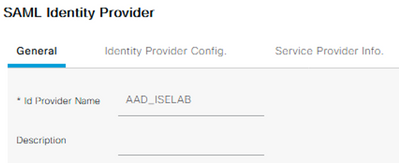
*** NOTE: At the time of this writing, ISE cannot create more than one SAML Id Provider with the same Azure tenant ID.
ISE Policy Elements and BYOD Portal
Step 2 – Create an Allowed Protocols list for MAB (if one is not already created)
Navigate to Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authentication > Allowed Protocols and click Add

Input the Name and optional Description, select only the Process Host Lookup option, and click Submit.

Step 3 – Create an Endpoint Identity Group for the BYOD endpoints
Navigate to Administration > Identity Management > Groups > Endpoint Identity Groups and click Add.
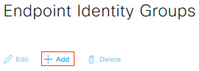
Input the Name and optional Description and click Submit.
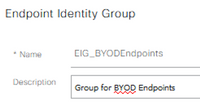
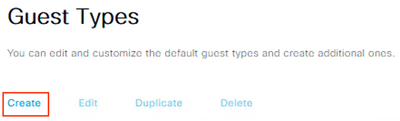
Step 4 – Configure a Guest Type for the BYOD users
Navigate to Work Centers > Guest Access > Portals & Components > Guest Types and click Create.
Input the Guest Type Name and optional Description
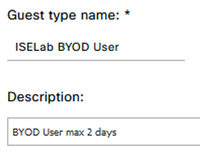
Under the Login Options section, select the Endpoint Identity Group previously created.
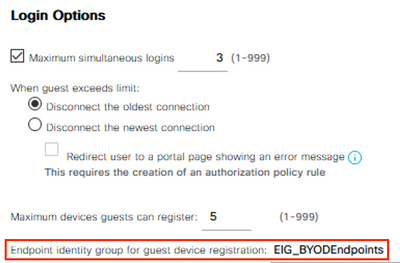
Configure all other preferred settings and click Save.
Step 5 – Configure the BYOD Portal
Navigate to Work Centers > Guest Access > Portals & Components > Guest Portals. Create a new Sponsored Guest Portal or select an existing one.
Input the Portal Name and optional Description.

In the Portal Settings section, select the SAML IdP from the ‘Authentication method’ drop-down list and the Guest Type from the ‘Employees using this portal as guests…’ drop-down list.
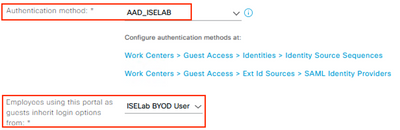
Configure all other preferred settings and click Save.
Entra ID SAML SSO Configuration
Step 6 – Export the SAML IdP info from ISE
Navigate to Administration > Identity Management > External Identity Sources > SAML Id Providers and Edit the IdP.
Select the Service Provider Info tab and click Export.
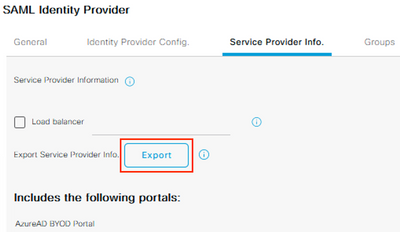
Save and extract the zip file and open the XML file in a text editor. Record the following attribute values:
- entityID
- AssertionConsumerService Locations
Example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><md:EntityDescriptor xmlns:md="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:metadata" entityID="http://CiscoISE/655019f2-fa19-4517-a5f6-b59d3110830b"><md:SPSSODescriptor AuthnRequestsSigned="false" WantAssertionsSigned="true" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"><md:KeyDescriptor use="signing"><ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"><ds:X509Data><ds:X509Certificate>MIIF6jCCA9KgAwIBAgIQYH/EmAAAAACOrCYAdmBsQDANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADB5MSUwIwYDVQQD
...
snip
...
</ds:X509Data></ds:KeyInfo></md:KeyDescriptor><md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient</md:NameIDFormat><md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress</md:NameIDFormat><md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent</md:NameIDFormat><md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified</md:NameIDFormat><md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:WindowsDomainQualifiedName</md:NameIDFormat><md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:kerberos</md:NameIDFormat><md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:X509SubjectName</md:NameIDFormat><md:AssertionConsumerService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST" Location="https://192.168.120.180:8443/portal/SSOLoginResponse.action" index="0"/><md:AssertionConsumerService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST" Location="https://ise30-sa.ise.xxx.local:8443/portal/SSOLoginResponse.action" index="1"/></md:SPSSODescriptor></md:EntityDescriptor>
Step 7 – Create a BYOD Security Group in Entra ID
Login to the Entra ID Portal and navigate to Azure Active Directory > Manage > Groups
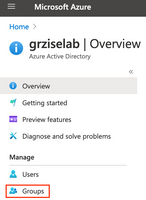
Click New Group

Configure the desired Group name, click the No members selected link and select the associated BYOD user accounts. Click Create.
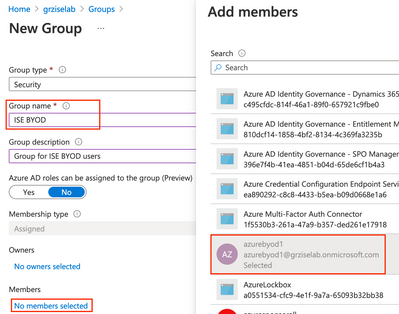
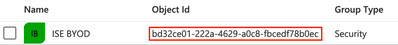
Record the Object ID for the new group.
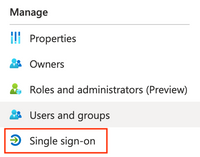
Step 8 – Register the Enterprise Application
Navigate to Azure Active Directory > Manage > Enterprise applications
Click on New Application

Click on Create your own application

Name the application and ensure the Non-gallery option is selected. Click Create.
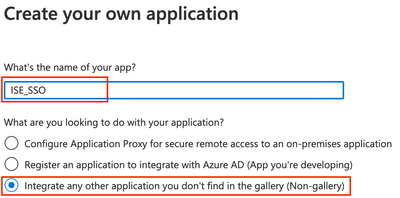
*** Note: A generic name was used as this application may also be used for other non-BYOD use cases in ISE.
Navigate to Manage > Users and groups
Click on Add user/group

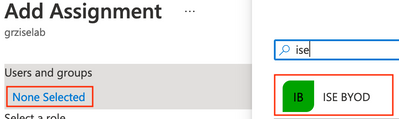
Under Users and groups, click on the link for None selected. Click the BYOD group created earlier and click Select.
Navigate to Manage > Single sign-on
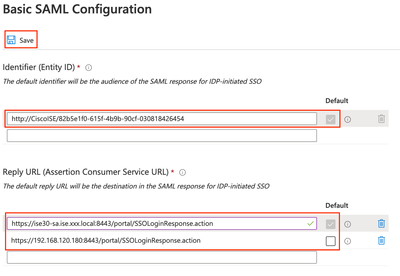
In the Basic SAML Configuration section, click Edit.
Paste the entityID and Location values recorded from XML file earlier in Step 6 and click Save.
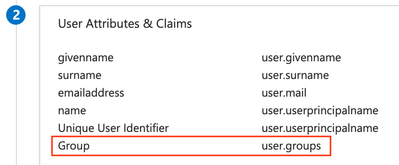
In the User Attributes & Claims section, click Edit.
Click on Add a group claim. Select the Security groups radio button and click Save.
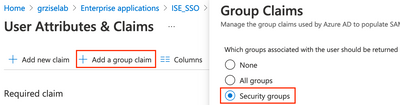
You should now see the Group claim added with a value of user.groups.
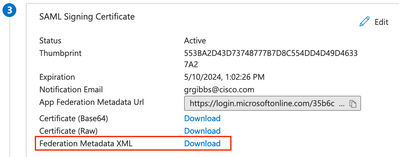
In the SAML Signing Certificate section, click the Download link for the Federation Metadata XML and save the file.
Complete the SAML Configuration in ISE
Step 9 – Configure the SAML IdP settings
Navigate to Administration > Identity Management > External Identity Sources > SAML Id Providers.
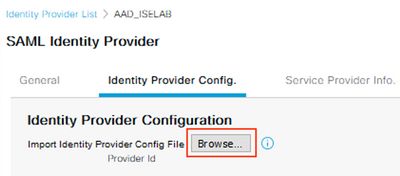
Select the SAML IdP and click on the Identity Provider Config tab.
Click the Browse button and select the Federation Metadata XML file downloaded from Azure in the previous step.
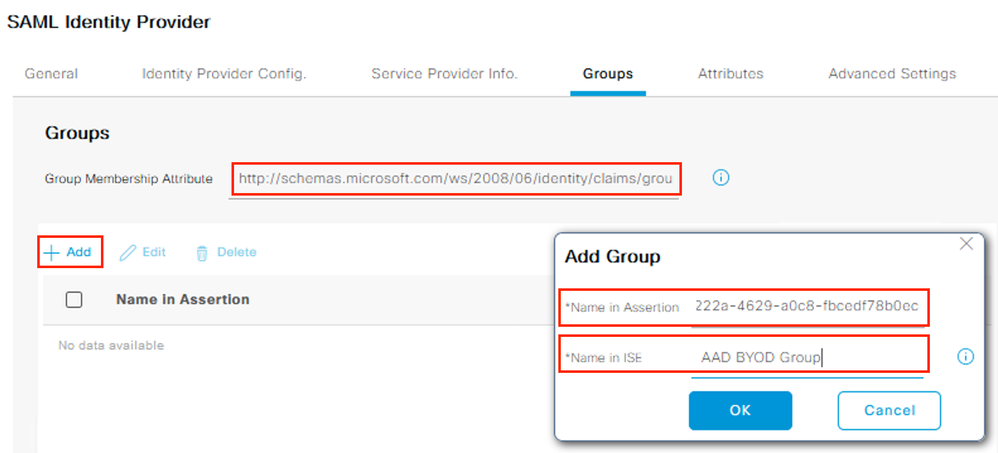
Select the Groups tab and input the following URL for the Group Membership Attribute.
Click the Add button. For the ‘Name in Assertion’ field, paste the Object ID copied from Azure in Step 7 and input a unique value for the ‘Name in ISE’ field. Click OK.
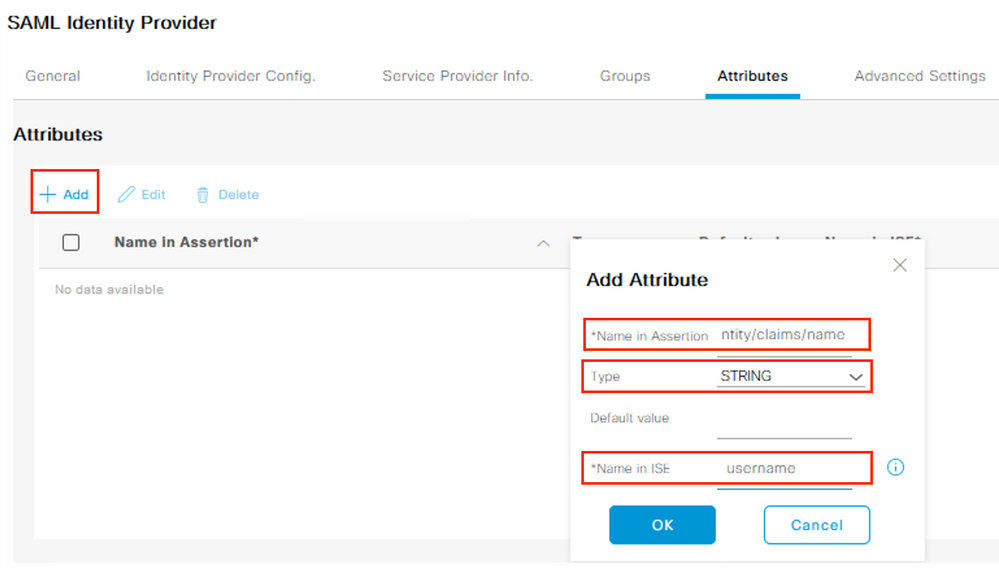
Select the Attributes tab and click Add. Input the following values and click OK.
|
Name in Assertion |
|
|
Type |
STRING |
|
Name in ISE |
username |
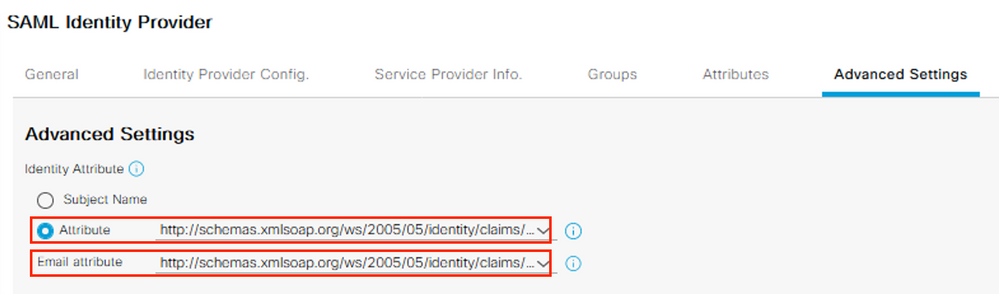
Select the Advanced Settings tab.
Under the Identity Attribute, select the Attribute radio button and select the available claims schema from the drop-down.
Select the same schema from the Email attribute drop-down. Click Save.
Complete the ISE Policy Configuration
Step 10 – Create the Authorization Profiles
Navigate to Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authorization > Authorization Profiles and click Add.
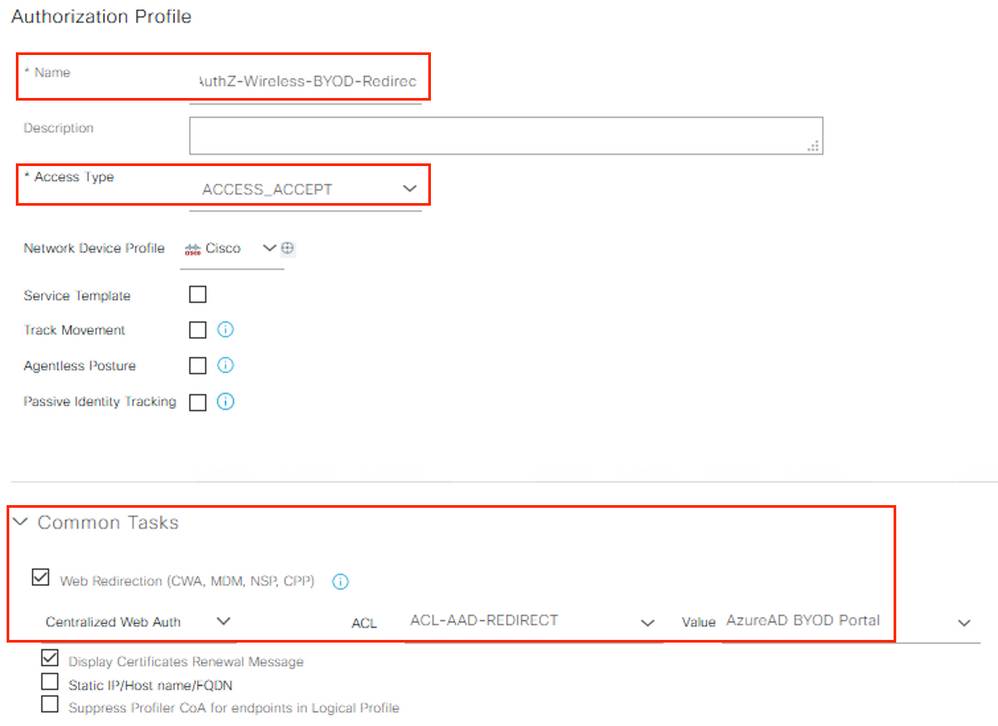
Create a new redirect Authorization Profile with the following values and click Submit.
|
Attribute |
Value |
Example Value |
|
Name |
<profile name> |
AuthZ-Wireless-BYOD-Redirect |
|
Description |
<optional description> |
|
|
Access Type |
ACCESS_ACCEPT |
|
|
Common Tasks |
|
|
|
Web Redirection (CWA, MDM, NSP, CPP) |
|
|
|
ACL |
<WLC ACL Name> |
ACL-AAD-REDIRECT |
|
Value |
<BYOD Portal Name> |
Azure BYOD Portal |
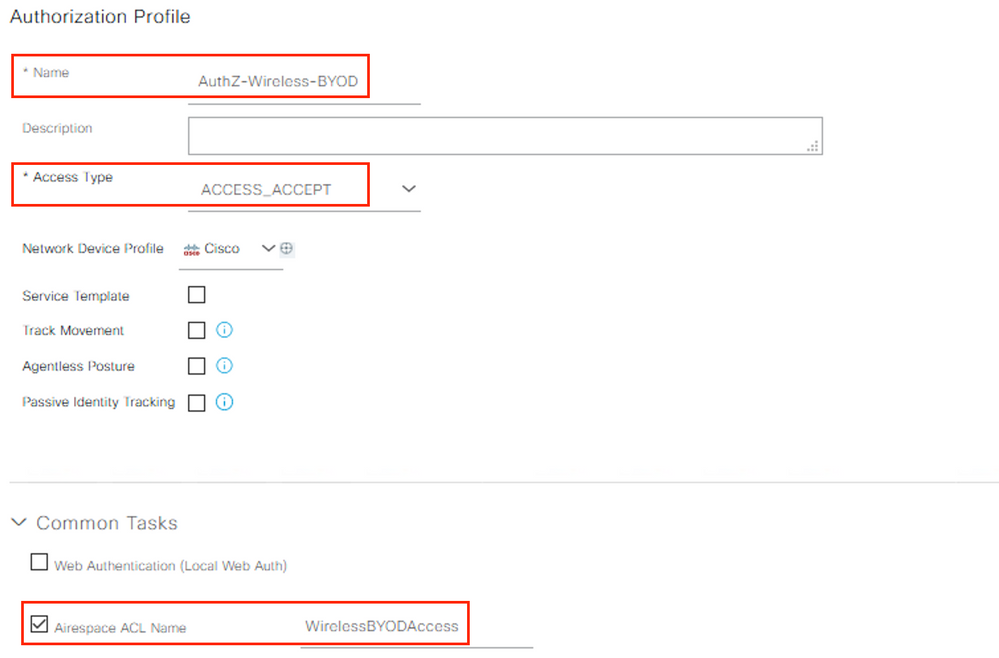
Create a new Authorization Profile to permit BYOD user access with the following values and click Submit.
|
Attribute |
Value |
Example Value |
|
Name |
<profile name> |
AuthZ-Wireless-BYOD |
|
Description |
<optional description> |
|
|
Access Type |
ACCESS_ACCEPT |
|
|
Common Tasks |
|
|
|
Airespace ACL Name |
<WLC ACL Name> |
WirelessBYODAccess |
Example:
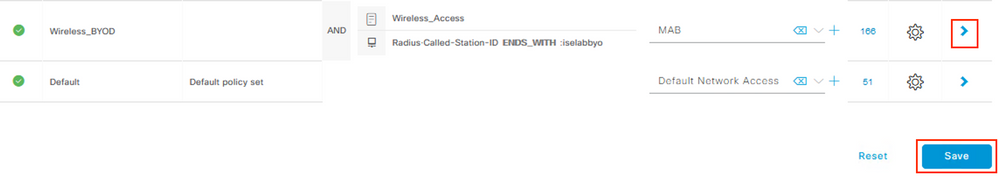
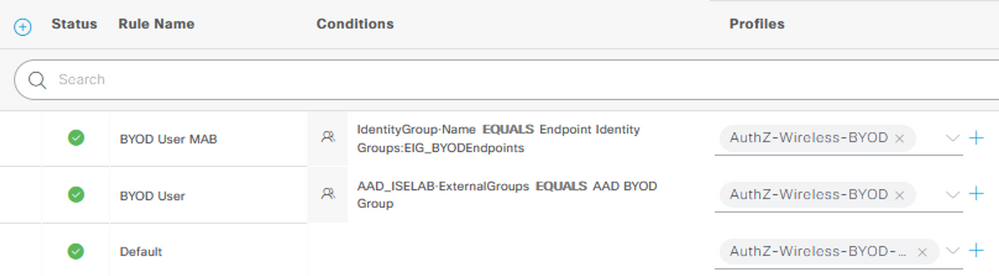
Step 11 – Create the Policy Set
Navigate to Policy > Policy Sets and create a new Policy Set matching the BYOD SSID. Select the Allowed Protocols list of MAB created earlier.
Click Save and then click the > symbol next to the new Policy Set.
Example:
Create a new Authentication Policy with a ‘Use’ value of Internal Endpoints. Click the dropdown for Options and set the ‘If User not found’ option to CONTINUE.
Example:
Create the Authorization Policies for the redirection and successful authorizations. Select the access AuthZ Profile created in Step 10 (e.g. AuthZ-Wireless-BYOD) for the access policies and the redirect AuthZ Profile (e.g. AuthZ-Wireless-BYOD-Redirect) for the Default policy. Click Save.
Example:
*** Note: The ‘BYOD User MAB’ policy shown above is to take advantage of the ‘Remember Me’ Guest feature. This policy can be skipped if this feature is not desired. See the ISE Guest Access Prescriptive Deployment Guide following link for more information on this feature.
Configure the Wireless LAN Controller
The following configuration settings are required on the Wireless LAN Controller. The sections below provide examples for both an AireOS based WLC (ex. 2504) and an IOS-XE based WLC (ex. 9800-CL).
AireOS WLC Configuration
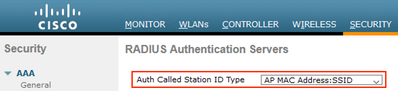
Configure the Wireless LAN Controller Called Station ID
On the WLC, navigate to Security > AAA > RADIUS > Authentication.
Ensure that the drop-down setting for ‘Auth Called Station ID Type’ includes the :SSID value.
*** Note: The above configuration is necessary to allow using the Policy Set matching condition for Called-Station-ID in Step 11.
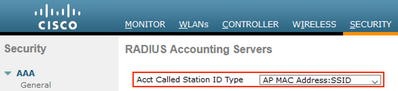
Navigate to Security > AAA > RADIUS > Accounting.
Ensure that the drop-down setting for ‘Acct Called Station ID Type’ includes the :SSID value.
Configure the Airespace ACLs used in the ISE Policies
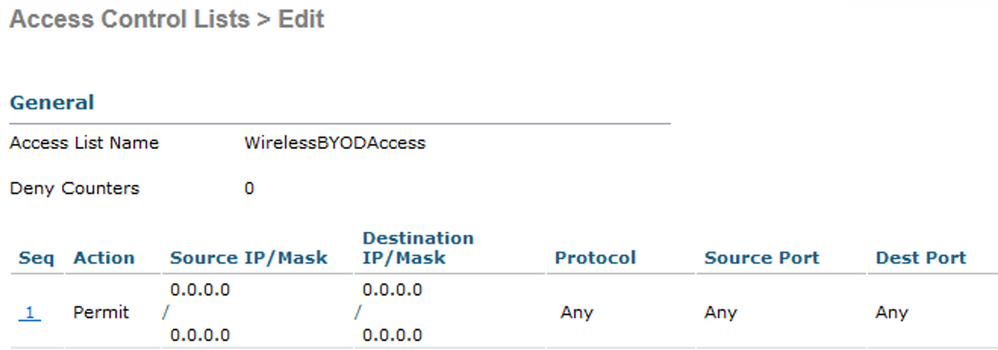
Navigate to Security > AAA > RADIUS > Access Control Lists > Access Control Lists.
Click New and create an Airespace ACL to permit the desired access for the BYOD users.
In this example, a simple ‘permit ip any any’ ACL is used.
Example:
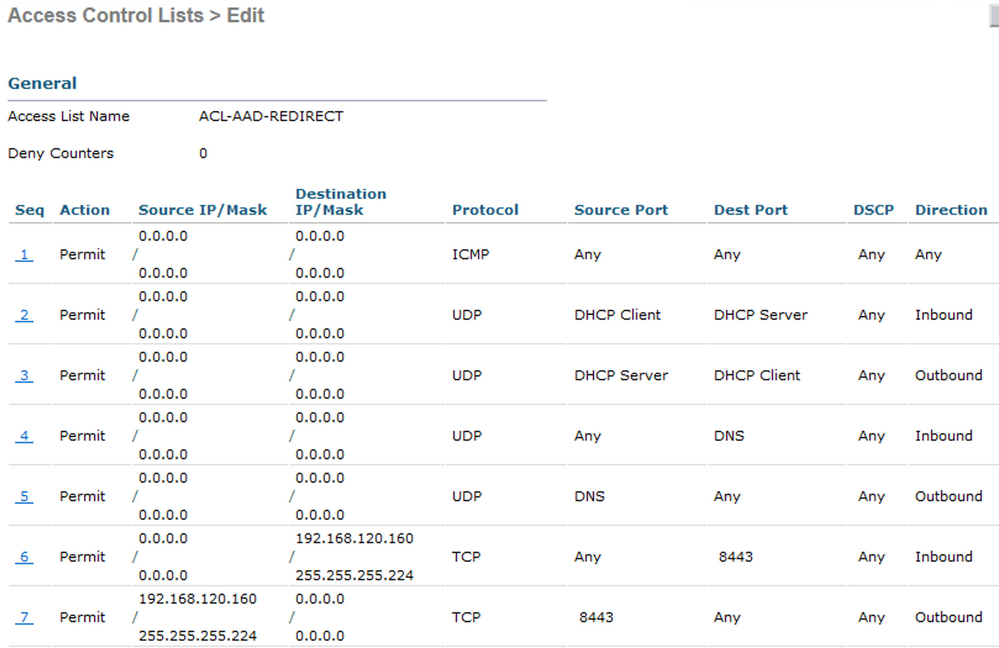
Click New and create an Airespace ACL for the URL redirection. At a minimum, the ACL should Permit (bypass redirection) for Inbound/Outbound traffic related to the following.
- DNS
- DHCP
- TCP/8443 traffic for the ISE BYOD Portal (unless a custom port was configured)
Example:
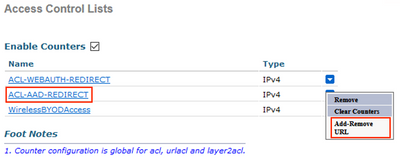
Return to the Access Control Lists page, click on the down-arrow next to the new redirect ACL and select Add-Remove URL.
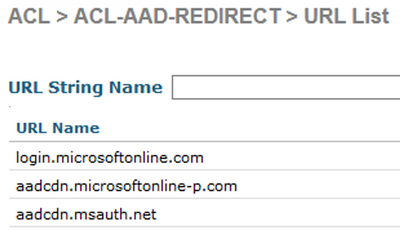
Add the following URL String Name values to exempt the traffic from redirection.
** July 2025: Updated list of URLs to work with Android and iPhone devices based on feedback from Community member @Danijel Turkovic
login.live.com go.microsoft.com aadcdn.msauth.net aadcdn.msftauth.net graph.microsoft.com app.vssps.dev.azure.com login.microsoftonline.com app.vssps.visualstudio.com login.microsoftonline-p.com management.core.windows.net secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com
Example:
IOS-XE WLC Configuration
Ensure the Called Station ID is configured to include the SSID name
This step is necessary if the ISE policy is using a matching condition that includes the SSID name.
In the WLC Admin UI, navigate to Configuration > Security > AAA and select the AAA Advanced tab. Click the Show Advanced Settings link, and select one of the options that includes 'ssid' for both the Accounting and Authentication options in the Called Station ID setting.
Example:
Configure the ACLs used in the ISE policies
Navigate to Configuration > Security > ACL and create the URL Redirect ACL be used. The 'deny' statements indicate that the traffic will be exempted from redirection and should include exemptions for DNS traffic as well as the relevant ISE portals.
Example:
Create a URL Filter to exempt the Microsoft FQDNs used in the SSO flow from redirection
Navigate to Configuration > Security > URL Filters, click Add and define the following settings:
- List Name = <name>
- Type = PRE-AUTH
- Action = DENY
- URLs = the below list of Microsoft URLs
** July 2025: Updated list of URLs to work with Android and iPhone devices based on feedback from Community member @Danijel Turkovic
login.live.com go.microsoft.com aadcdn.msauth.net aadcdn.msftauth.net graph.microsoft.com app.vssps.dev.azure.com login.microsoftonline.com app.vssps.visualstudio.com login.microsoftonline-p.com management.core.windows.net secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com
Example:
Add the URL Filter to the Policy associated with the WLAN
Navigate to Configuration > Tags & Profiles > Policy. Select the relevant Policy, at select the Access Policies tab.
In the URL Filters section, select the filter name created in the previous step for the Pre Auth setting (leave the Post Auth blank) and and click Update & Apply to Device.
Example:
Verify the configuration
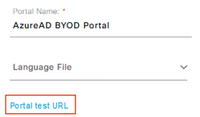
In ISE, navigate to Work Centers > Guest Access > Portals & Components > Guest Portals.
Select the BYOD Portal and click the Test portal URL link.
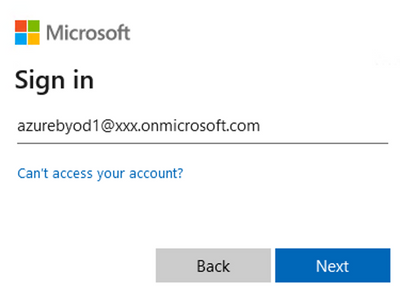
The browser will be redirected to the Microsoft login. Sign in with an Entra ID user account that is a member of the BYOD group created in Step 7.
Example:
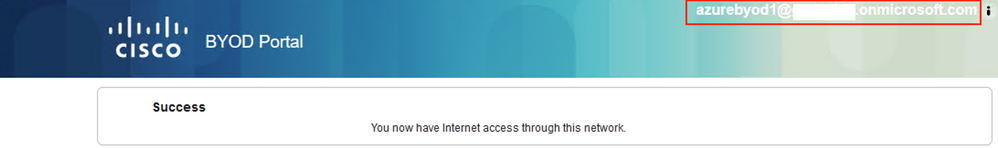
Depending on the settings configured for the BYOD Portal, you should see an AUP or Success page that includes the Entra ID login username.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Greg,
i strictly followed your excellent guide.
From test portal it works fine but does not work from a client
It looks like browser do not send back to ise the succesful repsonse it gets from azure
here you can find my issue
https://community.cisco.com/t5/network-access-control/ise-guest-portal-and-azure-sso/td-p/4471193
any help would be appreciated
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Your documentation has been a great help in testing ISE.
I have one question for you.
What is the license level of ISE required to apply this document?
Thanks
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@BeomYong Park, all you need is Essentials
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Greg Gibbs , thank you for the great guide, can I check if there is any guide that is using Catalyst 9800 as it is vastly different from AireOS?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Greg,
Thank you so much for designing and sharing this—it has been incredibly helpful in getting me started down this path.
I’ve been implementing your design for my company’s BYOD employee network, and I have about 95% of it working. However, I’m running into an issue with layering in Azure 2FA into the authentication stream. After entering my username and password, I get the “Our company requires more” screen, but the process seems to hang after that.
I’ve reviewed the necessary URLs listed in the Azure portal and added them to the URL filter, hoping that would resolve the issue in the pre-auth stage. However, the problem persists. I’ve also opened a TAC case and provided PCAPs, but we’re currently stalled.
Have you encountered this issue before, or do you have any suggestions for troubleshooting this further?
Thanks in advance for your time!
John Palmason
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@John Palmason, I did some testing with a Win11 Surface tablet as well as an iPhone.
With the Surface tablet, I was able to get the Authenticator enrolment flow working by adding the following two FQDNs to my pre-auth URL Filter.
- mysignins.microsoft.com
- account.activedirectory.windowsazure.com
With the iPhone, I tried adding multiple FQDNs documented here to my URL Filter, but nothing I did seemed to work. My guess is that there may be some additional endpoint specific URLs or recursive FQDNs used by Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) that are causing issues with the captive portal.
My only suggestion would be one or more of the following:
- Capture traffic to/from the endpoint when connected to a network that does not use a captive portal. Find all of the DNS lookups and FQDNs involved and try adding them to the URL Filter (this could easily get unwieldily)
- Contact Microsoft to see if they have a more specific list of ports, protocols, and FQDNs used specifically by the Authenticator enrolment flow
- Use Conditional Access to remove the requirement for MFA for users using this flow (tied to the App Registration)
- Communicate to your BYO users the steps to enroll with MFA from any internet connection prior to connecting to the company BYO network
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello Greg, thank you so much for your suggestions, I added the two URL's you suggested to my URL filter and also asked the Azure team to back off 2FA for this application to test it for the work flows. I had previously also just testing the SSID without mac address Auth to prove the WLC settings where working.
Once 2FA was removed, the login's worked perfectly and we have been able to successfully test our complete flow through ISE policies etc.
So its fully working as you described in your article of us now, because part of this requirements for this external guest flow was to make it easy to use and connect, we are going to leave the 2FA requirements off for this application.
So I haven't bothered to test it out fully with packet captures etc. as you have suggested. I did add some of the URL's from the same Azure FQDN's document before posting here and found it strange impacts on the captive not loading or taking very long time to process etc., so I striped it back to only the ones suggested in the base article and the two news and everything seems to working smoothly for now.
Thank you again for the quick reply, it was super helpful and I will use this to reflect the value add that Cisco support teams adds to the community users groups like this one.
John Palmason
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Is it correct to have the DENY action on the Url Filter list?
Can you also post the WLC 9800 Policy configuration details to have a complete scenario?
It should be configured with NAC State enabled.
When a device connects to the SSID, it will be redirected to the ISE Portal and applied the redirect ACL. Then the ISE portal will redirect user to login.microsoftonline.com and this is allowed by the Url Filter with DENY action in pre-auth?
During all this time the user will be seen as Web Auth Pending on WLC, right?
Thank you
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
hi @John Palmason @Greg Gibbs Thanks for the detailed steps on how to use SAML 0365 for the auth method. We are able to follow this and working as expected on PC's and Android devices. But problem we are facing with Apple iPhones, as we are using MSFT authenticator app for the multifactor / push notification as a secondary method, when the push notifications comes to iPhone, Authentication app is also opening with the push notification, After completing the push notification, Authenticator app is not closing, because of this backend live session is getting broke.
On the Android devices, we don't see authenticator app is opening with the push message.
Is there a way we can avoid this on the iphones, ?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
As @Greg Gibbs mentioned in another post, Cisco ISE does not support 2 SAML connections agains the same Azure Org, so having Admin Access SSO and BYOD Guest portal via Azure SSO must use the same one.
Working with TAC on an issue where some Admin users weren't able to be authenticated (all belonging to the same Group), we have detected the problem was in Step #8, when selecting "Click on Add a group claim. Select the Security groups radio button". The problem was due to the large number of groups that exist in our Entra ID organization, and because of a current limitation in Entra ID. If the group that the user is member of is not between the ones that are retrieved without reaching the limit of maximum groups that can be checked in Entra ID, it will be rejected and SAML response won't include any Group.
The solution has been to modify Step #8 with "Click on Add a group claim, and Select the Groups assigned to the application radio button.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Now, related to this guide, the setup is not working for me using C9800 WLC running 17.12.5, with anchored SSID.
I've reviewed all the settings in both ISE and WLC, and they are all good, in both the foreign and anchor WLCs where the WLAN profile and ACLs are cloned, and pre-auth-ACL assigned to Flex profile, and with pre-auth-ACL-URL filter assigned to the policy profile.
The problem I see is that users connect without been redirected to the login page at all, but they hit the authorization policy that should redirect them. this is confirmed in ISE, and with the WLC debug logs, but they are not redirected.
Side question but maybe related to this issue that I have, shoul this "WirelessBYODAccess" ACL be the redirect ACL that we created? There is no coincidence with the pre-auth-ACL created on this guide which may lead to errors.
|
Attribute |
Value |
Example Value |
|
Name |
<profile name> |
AuthZ-Wireless-BYOD |
|
Description |
<optional description> |
|
|
Access Type |
ACCESS_ACCEPT |
|
|
Common Tasks |
|
|
|
Airespace ACL Name |
<WLC ACL Name> |
WirelessBYODAccess |
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Awesome, Thank You for sharing!!!
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: