- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Knowledge Base
- T1/PRI line clock design considerations on ISR4K
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-06-2016 10:51 PM - edited 03-12-2019 10:24 AM
Introduction
When using digital voice interfaces like T1 CAS and PRI on Voice GW, attention needs to be paid to clock synchronization. In an event the clock is not accurately synchronized, line slips might occur and cause issues with audio quality and faxing.
In this document, we will explain how to approach clock synchronization on the ISR 4K.
1.Digital Voice Interface module on the ISR4K
Voice is processed by the DSP(PVDM4)that is inserted in the NIM-xMFT-T1/E1 module used in ISR 4K.
The Backplane Clock Mux can be used to synchronize the clock between modules, but it is not necessary to synchronize the clock with the backplane.
If you design the clock such that every module belongs to a different clock domain, the module can be connected to different devices providing different clocks.
2.Command to synchronize clock on ISR4K
On ISR4K, clock can be synchronized with System level or Controller level commands.
(System level command)
network-clock synchronization automatic
Enables network clock synchronization (required command)
network-clock synchronization participate slot / subslot
Decides whether or not you want to synchronize the module with the backplane clock. Synchronization is enabled by default
network-clock input-source priority controller [t1|e1] slot/bay/port
Configures the clock source of the backplane
(Controller level command)
clock source line [primary|secondary]
Configures the clock source of the backplane
clock source network
Uses the backplane clock or the oscillator clock as the module clock source
Note: The command 'clock source internal' is used for data transmission, not for voice transmission.
3. Configuration examples for clock synchronization
Below we will provide examples for clock synchronization on ISR4K
Example 1: You want to use the line clock as the master clock and synchronize with the backplane.
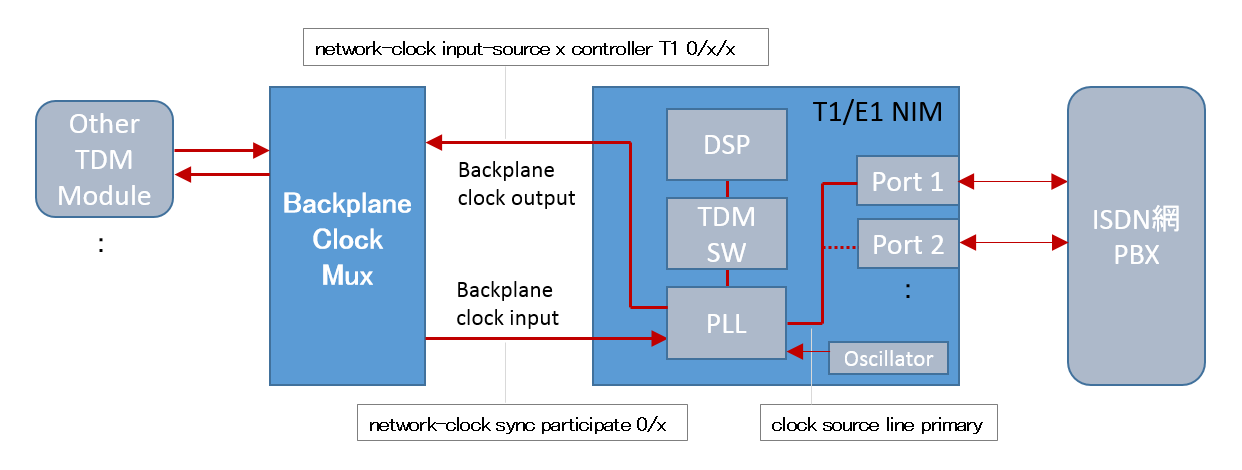
|
network-clock synchronization automatic network-clock synchronization participate 0/1 network-clock input-source 1 controller T1 0/1/0
controller T1 0/1/0 clock source line primary |
Example 2: You want to use the line clock as master, but not synchronize with the backplane

|
network-clock synchronization automatic no network-clock synchronization participate 0/1 network-clock input-source 1 controller T1 0/1/0
controller T1 0/1/0 clock source line primary |
Example 3: You want to use the backplane clock as the module clock source
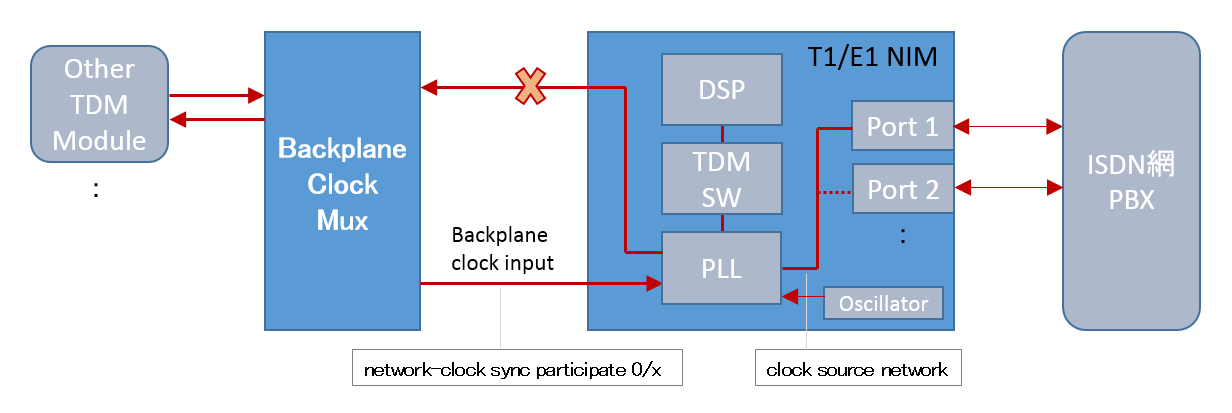
|
network-clock synchronization automatic network-clock synchronization participate 0/1 network-clock input-source 1 controller T1 0/1/0
controller T1 0/1/0 clock source network |
Conclusion
When using digital voice interfaces, clock synchronization need to be designed correctly. Audio quality issues or fax failures can happen as a result of wrong clock design.
Please understand the impact of the clock related commands on ISR4K and correctly configure the clock.
References
Network Synchronization for the Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi hishiyam,
Very nicely explained articale. We are in the position of using the ISR4321 as the network side. So we want to provide clocking to PBXs.
We do not want to take clocking from the line (end customer's PBX). In this scenarion the most logical approach is that in Example 3.
But in this case we get about 4 slips / 15 min.
Only if we use the example1 with "network-clock input-source 1 controller E1 0/2/0" can we stabalise the line in terms of slip and CRC errors. But we do not like Example 1 as it means that as a service provider we are relying on the PBXs to provide clocking and in certain cases this might be fine but in others with unreliable clocks this is not.
In the current constallation the NIM has two E1 going to the same PBX and slips happen on both E1 simultaniously.
Any thoughts on or advice. Many thanks, Donal
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Donal,
If you configure your ISR4321 to provide T1 clock (as clock master),
PBX or Telco should be configured to receive T1 clock from ISR4321.
Otherwise slip error will be observed on the T1 line.
You will need to consult with PBX vendor on the clock configuration
of the PBX.
If the PBX is connected with both ISR4321 and Telco, you need to take
care the clock synchronization design.
ISR4321 can support multiple clock domains (by using different NIMs),
but most of PBX can support single clock domain (by single TDM bus)
Possibe clock synchronization design are as follows.
Example 1: configure telco as clock master.
Telco -----------> PBX ----------> ISR4321
master slave master slave
Example 2: configure ISR4321 as clock master.
Telco <---------- PBX <---------- ISR4321
slave master slave master
I am not sure if Telco can receive clock from PBX.
Hiroshi
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
We are the Telco and connect into the core with SIP over either Fiber or VDSL
Core-SBC -------(SIP over Fiber or VDSL)----> ISR4321-----> PBX (two E1s on same NIM)
master -> slave
Our only way of getting to a No-Slips situation is by taking the clocking from the line. If we configure “Clock source Network” then we always have slips.
Regards
Donal
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
If the PBX is only connected with ISR4321 (via two E1s on the
same NIM), the PBX need to receive the clock from the line and
send E1 frame using the same clock.
Would it be possible for you to check the PBX's configuration.
(Is the PBX's line is configured as "slave clock" or "internal clock"?)
Hiroshi
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
I have configured 3 E1 isdn PRI located at one NIM-1MFT-T1/E1 and one NIM-2MFT-T1/E1, like the required is that the ISR4331 acts as isdn network side I have configured clock as you indicate in example 3 but I have a lot of sleeps in the 3 controllers.
Wich can be the problem.
Thank you very much in advance for your attention.
Best regards.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi all,
I have found this note in the chapter 'Network Synchronization for the Cisco 4000 Series ISRs' into the document 'Configuring the Cisco Fourth-Generation T1/E1 Voice and WAN Network Interface Module'
That seams different that you is suggesting on example 3, in fact, I have applied the 'no network clock participate' command for the two slots where I have the NIM cards an 'sleeps` have been reduced drastically, but still exists, now, I get a couple of 'sleeps' per hour.
I do not understand why, if router is providing clock, I getting 'sleeps' in the controllers.
Thank you in advanced for your answer.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey Everyone,
Can anybody tells what would be the appropriate solution for the below customer query
"We have 2 routers, each with 2 back-to-back PRIs, these routers are configured as the network side and is supposed to provide clocking to the remote PBX.
PRIGW-VG01-003006-01SE#sh run | s 0/1/0|0/2/0
controller T1 0/1/0
framing esf
clock source network
linecode b8zs
cablelength long 0db
pri-group timeslots 1-24
controller T1 0/2/0
framing esf
clock source network
linecode b8zs
cablelength long 0db
pri-group timeslots 1-24
interface Serial0/1/0:23
no ip address
encapsulation hdlc
isdn switch-type primary-ni
isdn protocol-emulate network
isdn incoming-voice voice
isdn supp-service name calling
isdn outgoing display-ie
trunk-group VESTA
interface Serial0/2/0:23
no ip address
encapsulation hdlc
isdn switch-type primary-ni
isdn protocol-emulate network
isdn incoming-voice voice
isdn supp-service name calling
isdn outgoing display-ie
trunk-group VESTA
The first PRI doesn’t have clocking issues, the other one does.
PRIGW-VG01-003006-01SE#sh controller t1
T1 0/1/0 is up
Applique type is Channelized T1
Cablelength is long gain36 0db
No alarms detected.
alarm-trigger is not set
Soaking time: 3, Clearance time: 10
AIS State:Clear LOS State:Clear LOF State:Clear
Framing is ESF, Line Code is B8ZS, Clock Source is Network.
BER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6
Data in current interval (599 seconds elapsed):
0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations
0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins
0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs
Total Data (last 24 hours)
0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations,
0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins,
0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs
T1 0/2/0 is up
Applique type is Channelized T1
Cablelength is long gain36 0db
No alarms detected.
alarm-trigger is not set
Soaking time: 3, Clearance time: 10
AIS State:Clear LOS State:Clear LOF State:Clear
Framing is ESF, Line Code is B8ZS, Clock Source is Network.
BER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6
Data in current interval (134 seconds elapsed):
0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations
1 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins
1 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs
Total Data (last 24 hours)
0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations,
749 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins,
749 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs
What we want is to verify how the clocking is supposed to be configured in this scenario. These “circuits” are on different NIMs and hence are consider their own clocking domain, but since they connect to the same remote device, they need to be in sync.
NAME: "NIM subslot 0/1", DESCR: "NIM-4MFT-T1/E1 - T1/E1 Serial Module"
PID: NIM-4MFT-T1/E1 , VID: V04 , SN: FOC213550N8
NAME: "NIM subslot 0/2", DESCR: "NIM-1MFT-T1/E1 - T1/E1 Serial Module"
PID: NIM-1MFT-T1/E1 , VID: V04 , SN: FOC21374Q0E
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Neeragu Good morning Neeragu, i've got the same issue.
1 router with 2 E1 port to connect 2 legacy PBX. I need to configure both E1 port to generate same clock for PBX ( that take clock from line) but on one of this i've got slip error.
If i use a Cisco 2911 all works like a charm.
Did you solve the issue? Could yo
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hiroshi
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community:

