- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Switching
- Re: ipsec AH in transport mode ,AH in tunnel mode
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-27-2012 08:37 PM - edited 03-07-2019 09:43 AM
Hi everybody.
I am reading about Ipsec which contains two major protocols among others: AH and ESP.
For now, I am focused on AH only. I read the theory on AH and two modes AH can operate : Transport mode and tunnel mode.
(201.201.201.1)h1--------R1(199.199.199.1) s0--------------------------------------------------------s0(199.199.199.2)R2-------H2( 200.200.200.2)
I want to implement the following:
Every time R1 receives ip packet from H1 destined for H2, R1 should use AH in transport mode before it sends the packet out to R2, Similarly, R2 should use AH in transport for packets sent by H2 to H1, before sending them to R1.
I just need an example as to how we can configure R1 and R2 to accomplish the above task..
Thanks for your help and have a great day.
.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Other Switching
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 12:58 AM
Hi Sara,
Please find the configuration sample for the GRE IPsec VPN using transport mode.
(201.201.201.1)h1--------R1(199.199.199.1) s0---------------------------s0(199.199.199.2)R2-------H2( 200.200.200.2)
You can use the ACL to restrict only to the required ports that needed for the vpn like udp 500, ah, gre and 4500 and you can check. Hope this helps.
Also you can refer the belwo mentioned site for much better understanding about the differences between transport or tunnel mode.
R1:
===
version 12.4
!
hostname R1
!
ip cef
!
!
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
crypto isakmp key CISCO address 199.199.199.2
!
crypto ipsec transform-set MyTransSet esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile MyProfile
set transform-set MyTransSet
!
interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
tunnel source 199.199.199.1
tunnel destination 199.199.199.2
tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
tunnel protection ipsec profile MyProfile
!
interface serial0
ip address 199.199.199.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 199.199.199.2
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
!
end
======================================================================
R2
=====
version 12.4
!
hostname R2
!
!
!
ip cef
!
!
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
crypto isakmp key CISCO address 199.199.199.1
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set MyTransSet esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile MyProfile
set transform-set MyTransSet
!
interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
tunnel source 199.199.199.2
tunnel destination 199.199.199.1
tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
tunnel protection ipsec profile MyProfile
!
interface serial0
ip address 199.199.199.2 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 199.199.199.1
!
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
!
end
Please do rate if the given information helps.
By
Karthik
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 01:21 AM
You can't configure that in Transport-mode. For IPSec (both AH and ESP) you have the following rule:
Transport-mode can only be used if the device that generated the packet also protects it and the device that verifies/decrypts it is the same that also processes the packet.
If you have security-gateways (R1 and R2) then you need two IP-headers. One for the end-to-end communication (with H1 and H2) and one for the gateway-to-gateway-communication (with R1 und R2). But Transport-mode uses the original IP-header so that can't work.
--
Don't stop after you've improved your network! Improve the world by lending money to the working poor:
http://www.kiva.org/invitedby/karsteni
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 11:15 AM
We want R1 to use AH in transport mode before sending out the above packet of s0. How can we configure AH in transport mode on R1 and R2?
You have to configure that the old way with crypto-maps. The tunnel-interfaces always use ipsec-tunnel-mode regardless what you configure in your transform-set.
--
Don't stop after you've improved your network! Improve the world by lending money to the working poor:
http://www.kiva.org/invitedby/karsteni
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-29-2012 12:44 AM
Hi Sara,
I forget to mention the website info in my earlier post!!! Very welll explained scenario about the modes!!!
http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/protocols/870-ipsec-modes.html
Please do rate if the given information helps.
By
Karthik
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-29-2012 02:06 AM
Hi Karthik,
> I forget to mention the website info in my earlier post!!! Very welll explained scenario about the modes!!!
> http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/protocols/870-ipsec-modes.html
The explaination of Transport-mode on that website is comlpetely wrong and shouldn't be referenced. Section 4.5 of RFC 2401 shows how the headers are build for tunnel- and transport-mode.
Sent from Cisco Technical Support iPad App
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-29-2012 02:40 PM
After being at the right PC now, here is an example for using AH with transport-mode (R1 shown, R2 is similar):
!
crypto isakmp key cisco address 2.2.2.2
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set AH ah-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto map VPN local-address Loopback1
crypto map VPN 1 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 2.2.2.2
set transform-set AH
match address VPN-R2
!
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
crypto map VPN
!
ip route 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2
!
ip access-list extended VPN-R2
permit ip host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2
And that is what flows over the wire with a ping:
Frame 14: 138 bytes on wire (1104 bits), 138 bytes captured (1104 bits)
Ethernet II, Src: ca:00:36:91:00:08 (ca:00:36:91:00:08), Dst: ca:01:36:91:00:08 (ca:01:36:91:00:08)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1), Dst: 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Authentication Header
Next Header: ICMP (0x01)
Length: 24
AH SPI: 0x87018e79
AH Sequence: 2
AH ICV: 389141bfef53445fbd77452c
Internet Control Message Protocol
Type: 8 (Echo (ping) request)
Code: 0
Checksum: 0x63fa [correct]
Identifier (BE): 0 (0x0000)
Identifier (LE): 0 (0x0000)
Sequence number (BE): 2 (0x0002)
Sequence number (LE): 512 (0x0200)
[Response In: 15]
Data (72 bytes)
0000 00 00 00 00 00 02 1a 4c ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd .......L........
0010 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0020 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0030 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0040 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ........
Data: 0000000000021a4cabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcd...
[Length: 72]
--
Don't stop after you've improved your network! Improve the world by lending money to the working poor:
http://www.kiva.org/invitedby/karsteni
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-30-2012 01:17 AM
1) The "crypto-isakmp" commands don't specify to use tunnel mode or not. That's done in the "crypto ipsec transform-set". The ISAKMP-commands specify the parameters for the setup of the ISAKMP-tunnel. You can look at this tunnel as a management-connection between the two ipsec-peers. I skipped that because the router (starting with 12.4(20)T has usable defaults. You can see the defaults with "show crypto isakmp policy". The key is still needed to authenticate the connection-setup against Man-in-the-Mittle-attacks. Thats independent of using transport- or tunnel-mode.
2) The crypto-map is incomplete until you configure a "match address" and "set peer" statement. It just has to be there to work.
Sent from Cisco Technical Support iPad App
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 12:58 AM
Hi Sara,
Please find the configuration sample for the GRE IPsec VPN using transport mode.
(201.201.201.1)h1--------R1(199.199.199.1) s0---------------------------s0(199.199.199.2)R2-------H2( 200.200.200.2)
You can use the ACL to restrict only to the required ports that needed for the vpn like udp 500, ah, gre and 4500 and you can check. Hope this helps.
Also you can refer the belwo mentioned site for much better understanding about the differences between transport or tunnel mode.
R1:
===
version 12.4
!
hostname R1
!
ip cef
!
!
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
crypto isakmp key CISCO address 199.199.199.2
!
crypto ipsec transform-set MyTransSet esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile MyProfile
set transform-set MyTransSet
!
interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
tunnel source 199.199.199.1
tunnel destination 199.199.199.2
tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
tunnel protection ipsec profile MyProfile
!
interface serial0
ip address 199.199.199.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 199.199.199.2
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
!
end
======================================================================
R2
=====
version 12.4
!
hostname R2
!
!
!
ip cef
!
!
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
crypto isakmp key CISCO address 199.199.199.1
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set MyTransSet esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile MyProfile
set transform-set MyTransSet
!
interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
tunnel source 199.199.199.2
tunnel destination 199.199.199.1
tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
tunnel protection ipsec profile MyProfile
!
interface serial0
ip address 199.199.199.2 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 199.199.199.1
!
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
!
end
Please do rate if the given information helps.
By
Karthik
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 05:46 PM
Hi Karthik
R1:
===
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
crypto isakmp key CISCO address 199.199.199.2
!
crypto ipsec transform-set MyTransSet esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto ipsec profile MyProfile
set transform-set MyTransSet
!
interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
tunnel source 199.199.199.1
tunnel destination 199.199.199.2
tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
tunnel protection ipsec profile MyProfile
!
interface serial0
ip address 199.199.199.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 199.199.199.2
All the packets destined for 202.202.202.0 will be matched by static default route above which means R1 will use interface so to forward them. ipsec will not be used because packets are not directed to tunnel configured on R1.
If we want all the packets destined for 202.202.202.0/24 network to use ipsec, we must modify the static route above as shown below:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.2 ( which is the next hop address from tunnel 0 on R1)
Am I correct?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 01:21 AM
You can't configure that in Transport-mode. For IPSec (both AH and ESP) you have the following rule:
Transport-mode can only be used if the device that generated the packet also protects it and the device that verifies/decrypts it is the same that also processes the packet.
If you have security-gateways (R1 and R2) then you need two IP-headers. One for the end-to-end communication (with H1 and H2) and one for the gateway-to-gateway-communication (with R1 und R2). But Transport-mode uses the original IP-header so that can't work.
--
Don't stop after you've improved your network! Improve the world by lending money to the working poor:
http://www.kiva.org/invitedby/karsteni
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 09:27 AM
Thanks Karsten and Karthik.
You can't configure that in Transport-mode. For IPSec (both AH and ESP) you have the following rule:
Transport-mode can only be used if the device that generated the packet also protects it and the device that verifies/decrypts it is the same that also processes the packet.
I got it. I am trying to understand how we can configure AH in transport mode on a router.
R1(199.199.199.1)S0-----------------------------------S0(199.199.199.2)R2
R1 has Loopback1 1.1.1 R2 has Loopback 2.2.2.2
R1 sends a ping packet with src ip 1.1.1.1 ,dst ip 2.2.2.2.
We want R1 to use AH in transport mode before sending out the above packet of s0. How can we configure AH in transport mode on R1 and R2?
Thanks and have a great weekend.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 11:15 AM
We want R1 to use AH in transport mode before sending out the above packet of s0. How can we configure AH in transport mode on R1 and R2?
You have to configure that the old way with crypto-maps. The tunnel-interfaces always use ipsec-tunnel-mode regardless what you configure in your transform-set.
--
Don't stop after you've improved your network! Improve the world by lending money to the working poor:
http://www.kiva.org/invitedby/karsteni
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 03:23 PM
Hi Karsten
crypto ipsec transform-set MyTransSet esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
Above the mode is transport, if we do not specify the mode , what is the default mode ?
Thanks
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-28-2012 11:50 PM
> Above the mode is transport, if we do not specify the mode , what is the default mode ?
The default is tunnel-mode. That's what most of the time is needed on a vpn-gateway that protects the data of other systems.
Sent from Cisco Technical Support iPad App
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-29-2012 12:44 AM
Hi Sara,
I forget to mention the website info in my earlier post!!! Very welll explained scenario about the modes!!!
http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/protocols/870-ipsec-modes.html
Please do rate if the given information helps.
By
Karthik
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-29-2012 02:06 AM
Hi Karthik,
> I forget to mention the website info in my earlier post!!! Very welll explained scenario about the modes!!!
> http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/protocols/870-ipsec-modes.html
The explaination of Transport-mode on that website is comlpetely wrong and shouldn't be referenced. Section 4.5 of RFC 2401 shows how the headers are build for tunnel- and transport-mode.
Sent from Cisco Technical Support iPad App
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-30-2012 09:00 AM
Thanks karsten!!! let me check the rfc definition and explaination for the same!!!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-30-2012 07:52 PM
HI Karsten,
Could you please explain me on the headers explained in rfc. I do not see any difference in opinion and am not sure if am missing anything.
RFC Says
===========
Case 1. The case of providing end-to-end security between 2 hosts
across the Internet (or an Intranet).
====================================
| |
H1* ------ (Inter/Intranet) ------ H2*
Note that either transport or tunnel mode can be selected by the
hosts. So the headers in a packet between H1 and H2 could looklike any of the following:
Transport Tunnel
----------------- ---------------------
1. [IP1][AH][upper]
4. [IP2][AH][IP1][upper] --> ( Method that explained in firewall forum)
2. [IP1][ESP][upper]
5. [IP2][ESP][IP1][upper]
3. [IP1][AH][ESP][upper]
Firewall forum says
===============
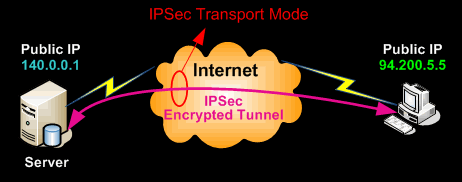
The packet diagram below illustrates
IPSec Transport mode
with
AH header
:
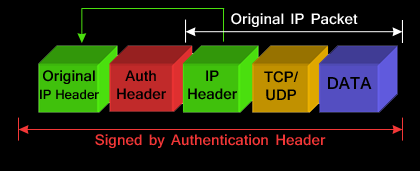
The AH can be applied alone or together with the ESP when IPSec is in transport mode. AH’s job is to protect the entire packet, however, IPSec in transport mode does not create a new IP header in front of the packet but places a copy of the original with some minor changes to the protocol ID therefore not providing essential protection to the details contained in the IP header (Source IP, destination IP etc). AH is identified in the New IP header with an IP protocol ID of 51.
By
Karthik
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-31-2012 12:37 AM
Hi Karthik,
The line that you quoted in bold is from the right column in the RFC where the tunnel-mode is shown. Nr. 1) is what we are talking about at the moment:
1. [IP1][AH][upper]
And there the problem is with the diagram and the explaination from your referenced site. In transport mode, the original header is used. The AH is placed between the IP-header and the upper layers. But no copy of the original header is used.
That can be seen in the capture:
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1), Dst: 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Version: 4
Header length: 20 bytes
Differentiated Services Field: 0x00 (DSCP 0x00: Default; ECN: 0x00: Not-ECT (Not ECN-Capable Transport))
Total Length: 124
Identification: 0x0001 (1)
Flags: 0x00
Fragment offset: 0
Time to live: 255
Protocol: AH (51)
Header checksum: 0xb548 [correct]
Source: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)
Destination: 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Authentication Header
Next Header: ICMP (0x01)
Length: 24
AH SPI: 0x87018e79
AH Sequence: 1
AH ICV: aaed169f7013d8ae9a3f2a7e
Internet Control Message Protocol
Type: 8 (Echo (ping) request)
Code: 0
Checksum: 0x640f [correct]
Identifier (BE): 0 (0x0000)
Identifier (LE): 0 (0x0000)
Sequence number (BE): 1 (0x0001)
Sequence number (LE): 256 (0x0100)
Data (72 bytes)
There is no inner IP-header. Only the original one. ICMP (the upper layer in my capture) follows directly behind the AH. The Protocol number in the original header is changed to 51 (AH) and the next-header field in the AH shows the protocol ICMP which was in the original IP-header.
--
Don't stop after you've improved your network! Improve the world by lending money to the working poor:
http://www.kiva.org/invitedby/karsteni
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-29-2012 02:40 PM
After being at the right PC now, here is an example for using AH with transport-mode (R1 shown, R2 is similar):
!
crypto isakmp key cisco address 2.2.2.2
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set AH ah-sha-hmac
mode transport
!
crypto map VPN local-address Loopback1
crypto map VPN 1 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 2.2.2.2
set transform-set AH
match address VPN-R2
!
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
crypto map VPN
!
ip route 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2
!
ip access-list extended VPN-R2
permit ip host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2
And that is what flows over the wire with a ping:
Frame 14: 138 bytes on wire (1104 bits), 138 bytes captured (1104 bits)
Ethernet II, Src: ca:00:36:91:00:08 (ca:00:36:91:00:08), Dst: ca:01:36:91:00:08 (ca:01:36:91:00:08)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1), Dst: 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Authentication Header
Next Header: ICMP (0x01)
Length: 24
AH SPI: 0x87018e79
AH Sequence: 2
AH ICV: 389141bfef53445fbd77452c
Internet Control Message Protocol
Type: 8 (Echo (ping) request)
Code: 0
Checksum: 0x63fa [correct]
Identifier (BE): 0 (0x0000)
Identifier (LE): 0 (0x0000)
Sequence number (BE): 2 (0x0002)
Sequence number (LE): 512 (0x0200)
[Response In: 15]
Data (72 bytes)
0000 00 00 00 00 00 02 1a 4c ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd .......L........
0010 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0020 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0030 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0040 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ........
Data: 0000000000021a4cabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcd...
[Length: 72]
--
Don't stop after you've improved your network! Improve the world by lending money to the working poor:
http://www.kiva.org/invitedby/karsteni
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-29-2012 06:51 PM
Hi Karsten
Please consider the partial configuration for tunnel mode below:
R1(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1
R1(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R1(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R1(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R1(config)#crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.2
above we have configuration related to formation of tunnel,( tunnel mode), According to above configuration, all negotiations will be authenticated using md5, encrypted by 3des, and the other end of tunnel must be configured with key firewallcx in order to form tunnel with R1.
But now when i look at your example for implementing AH in transport mode, I found:
crypto isakmp key cisco address 2.2.2.2
1)My question is since we don't have a tunnel mode here, so what is the purpose of configuring the key" cisco " above ?
=============================================================================================================
Please consider the partial configurations from your example:
crypto map VPN local-address Loopback1
crypto map VPN 1 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 2.2.2.2
set transform-set AH
match address VPN-R2
2)I understand in tunnel mode the " set peer 2.2.2.2" will cause router to use 2.2.2.2 as destination ip before packet is forwarded out of tunnel. But why do we have " set peer 2.2.2.2" in above configuration for AH in transport mode?
I really appreciate your help.
thanks and have a great day.
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide


