MAB or MAC Authentication Bypass is a mechanism that allow a non-capable 802.1X to access network by validating the presence or not of the mac address of the device in the local database of Cisco ISE.
MAB is not secure because, malicious user can unplug a legitimate printer and plug his PC, then modify the MAC address to be equal to the mac of the printer. The malicious user now is doing a MAC Spoofing attack.
Cisco ISE is armed with a mechanism or a feature called Anomalous Behavior Detection to detect potential MAC spoofing. With Anomalous What does Cisco ISE does? It checks data collected through profiling and compares data to look for contradictions or if there a change of profiling data for the MAC address. In order to accomplish this, Anomalous Behavior Detection checks the following:
Port type: The port type determines an endpoint’s method of access. For example, if a MAC address was originally used on a wired connection, that same MAC address should not be connecting to the wireless network. Even on the same computer, the wireless NIC should have a separate MAC address. This would be a clear indication that a MAC address is being spoofed.
DHCP Class-Identifier: This profiling attribute can help determine the type of client or vendor for an endpoint. If this changes for a detected endpoint, it could be an indication of a spoofed MAC address. For example, if an endpoint is configured with a static IP address, there should be no DHCP Class-Identifier attribute populated in ISE. If that MAC address is later spoofed and new endpoints used DHCP, ISE would detect that change as a potential anomalous behavior. Another example that would take it a step further is if a previously profiled endpoint used DHCP and the Class-Identifier was originally Cisco-Telepresence. If ISE later received the DHCP Class-Identifier MSFT 5.0 for that endpoint, this could also be an indication that the MAC address has been spoofed.
Endpoint policy: The profile policy for an endpoint is determined when ISE compares the collected profile attributes to the defined profiles and finds a match. The endpoint is assigned the endpoint policy. An example of anomalous behavior would be an endpoint being assigned the endpoint policy Cisco-IP-Phone-8831 that later changes to Windows7-Workstation for that MAC address. This kind of change might indicate that someone is spoofing the MAC address of the endpoint.
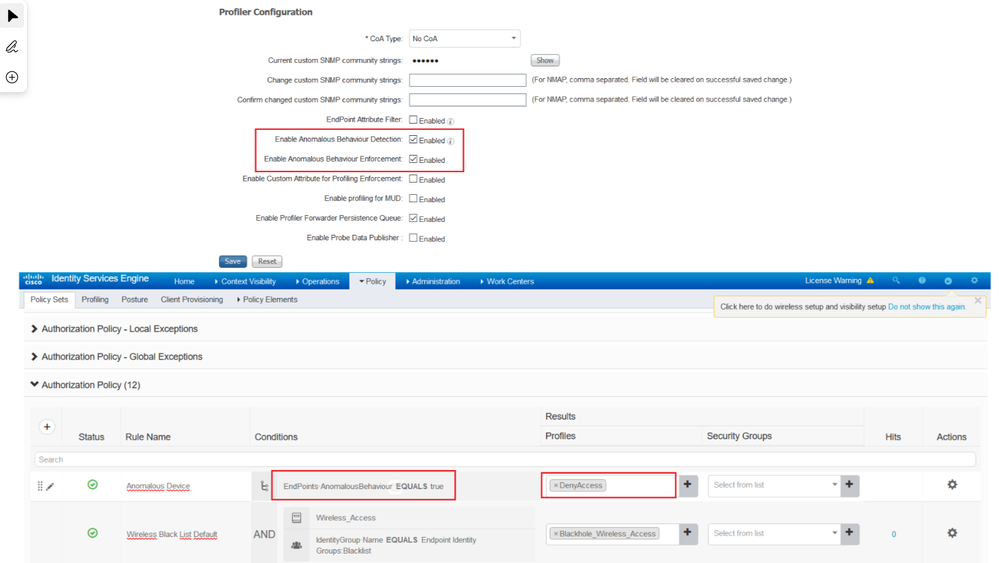
The Anomalous Behaviour Detection feature does not automatically change the network access of an endpoint when detected. If an endpoint sees certain profile data change, it sets the AnomalousBehaviour attribute for that endpoint to true. In order to change the network access based on Anomalous Behaviour Detection, Anomalous Behaviour Enforcement must be enabled. This allows ISE to issue a Change of Authorization (CoA) upon the detection of the anomalous behavior. The suspicious endpoints can then be reauthorized based on a configured authorization policy as shown below by using the condition “EndPoints: AnomalousBehavior EQUALS True” with the “DenyAccess” as the results or as the Authorization Profile.