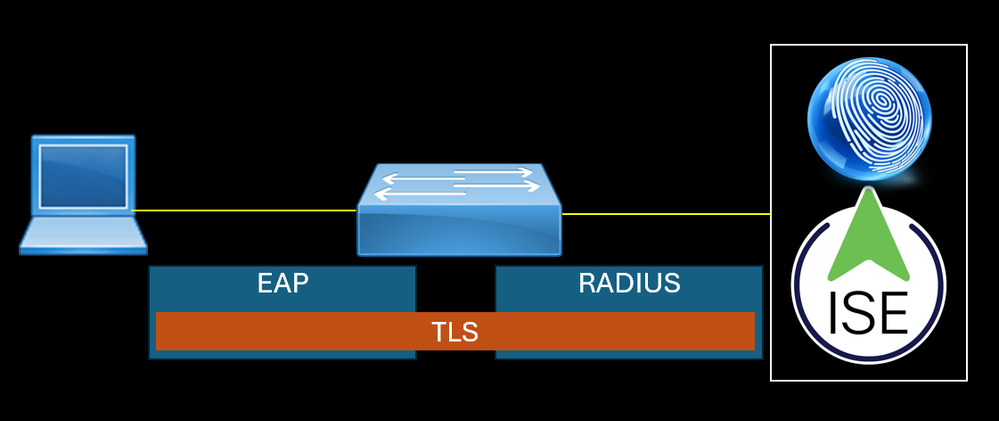
EAP runs over Layer 2 of the OSI model, the data link layer, and doesn't require Layer 3 IP connectivity.
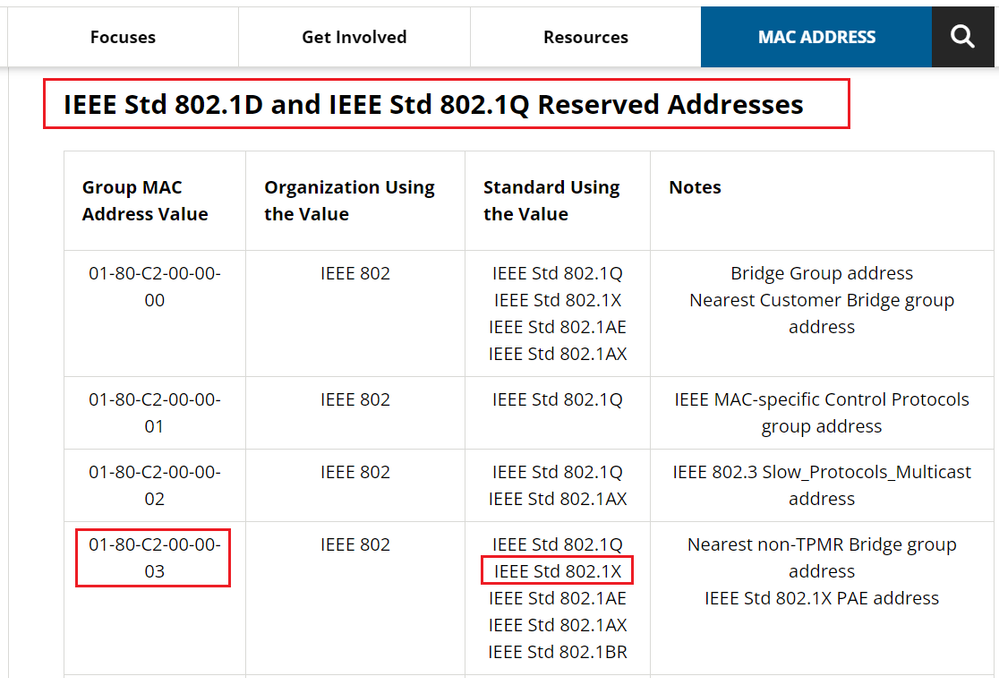
EAP Packet sent by the endpoint does not have L3 and L4 headers, the L7 data is encapsulated by EAP protocol with L2 informations. The source MAC address is the endpoint. For the destination MAC address, 802.1X uses the reserved multicast MAC address Nearest (01:80:c2:00:00:03).
PEAP is an outer method to secure the inner method such as MSCHAPv2. To do this, PEAP has two phases Phase 1 and Phase 2, the first phase is negociated to establish a secure TLS tunnel like the SSL Handshake for HTTPS traffic. The Second phase is used to negociate the client authentication process securely for example user identity (username) and the challenge response to verify the password.
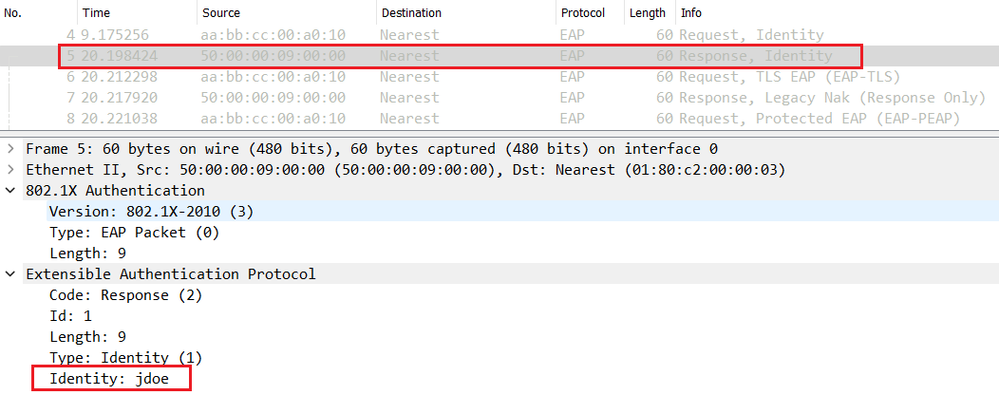
In the PEAP Phase 1, the endpoint sends an EAP Response-Identity message to answer the EAP Request-Identity sent by the NAD (Switch for example). The Supplicant can send the real username or anonymous as the username.
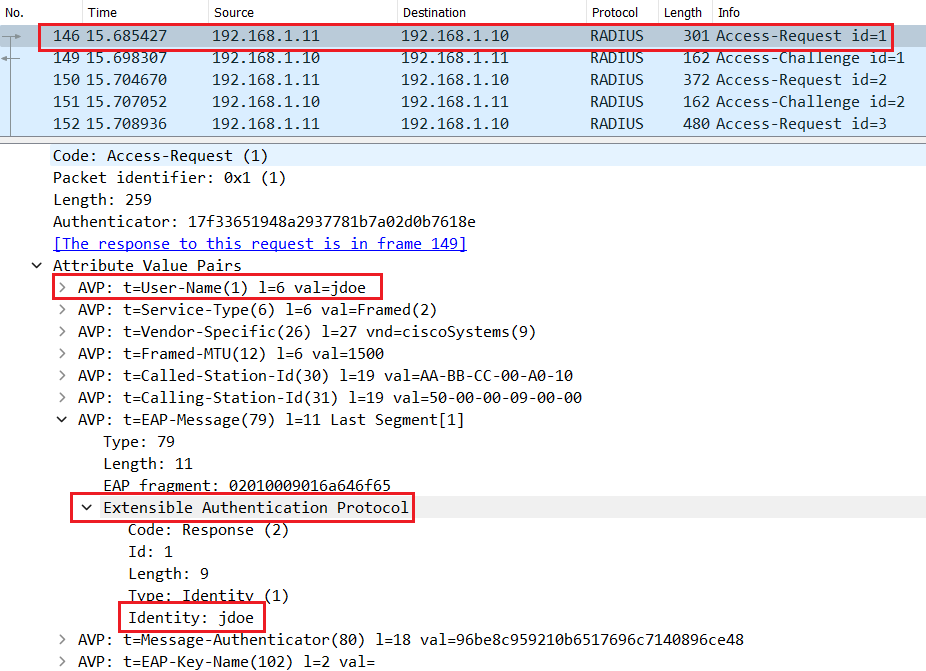
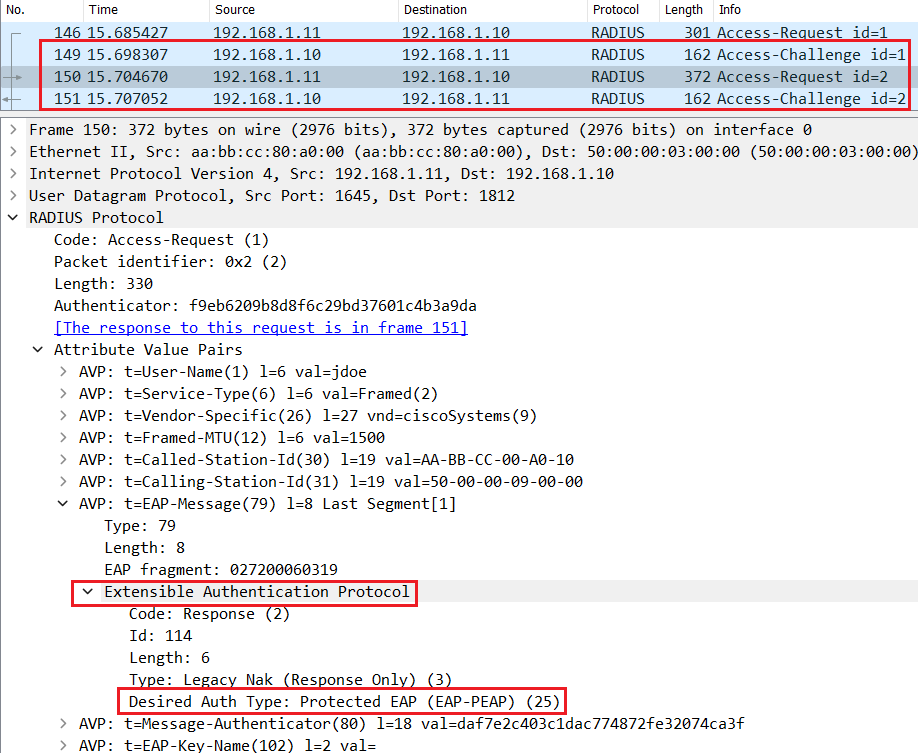
The Switch encapsulates the EAP packet with Layer 3 and Layer 4 headers to create a Radius Access-Request so that it can be routed to Cisco ISE.
Subsequent messages are exchanged to negociate the outer Method, PEAP in this case. As shown below both Endpoint and Cisco ISE agree to use PEAP as the desired inner method.
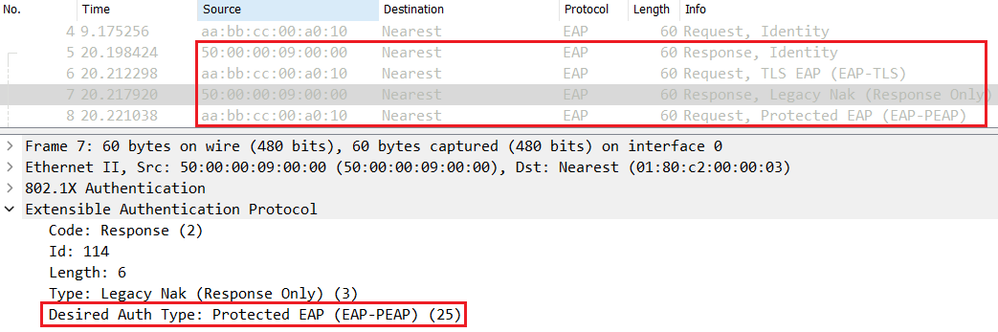
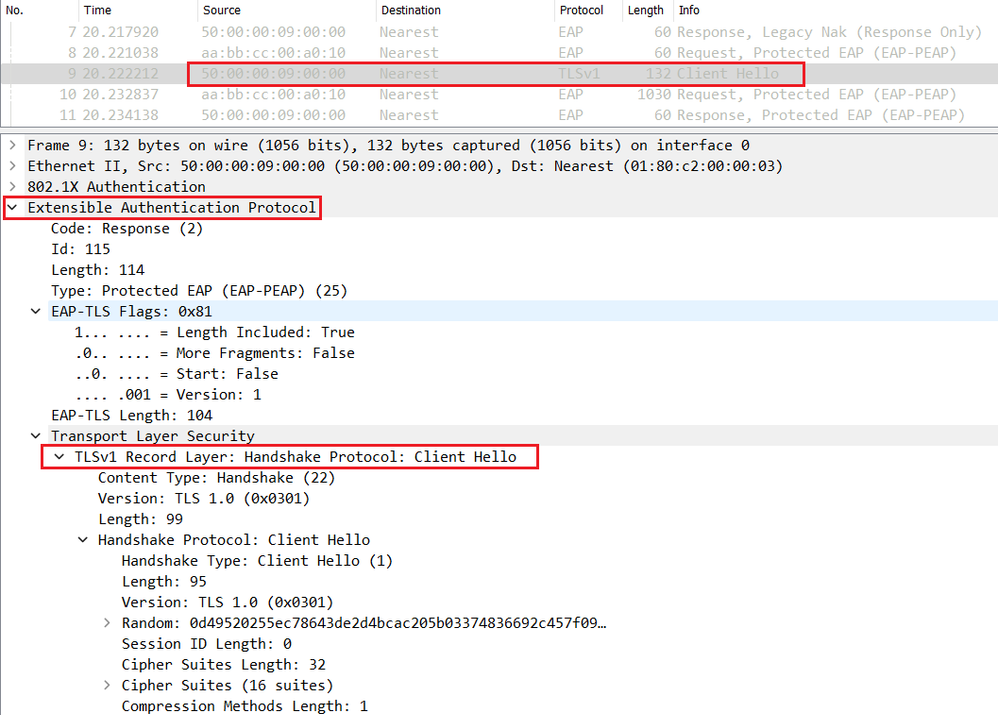
A this stage, the TLS negociation starts between the endpoint and Cisco ISE.
The endpoint sends a Client-Hello inside the EAP packet containing the supported ciphers (ciphersuites).
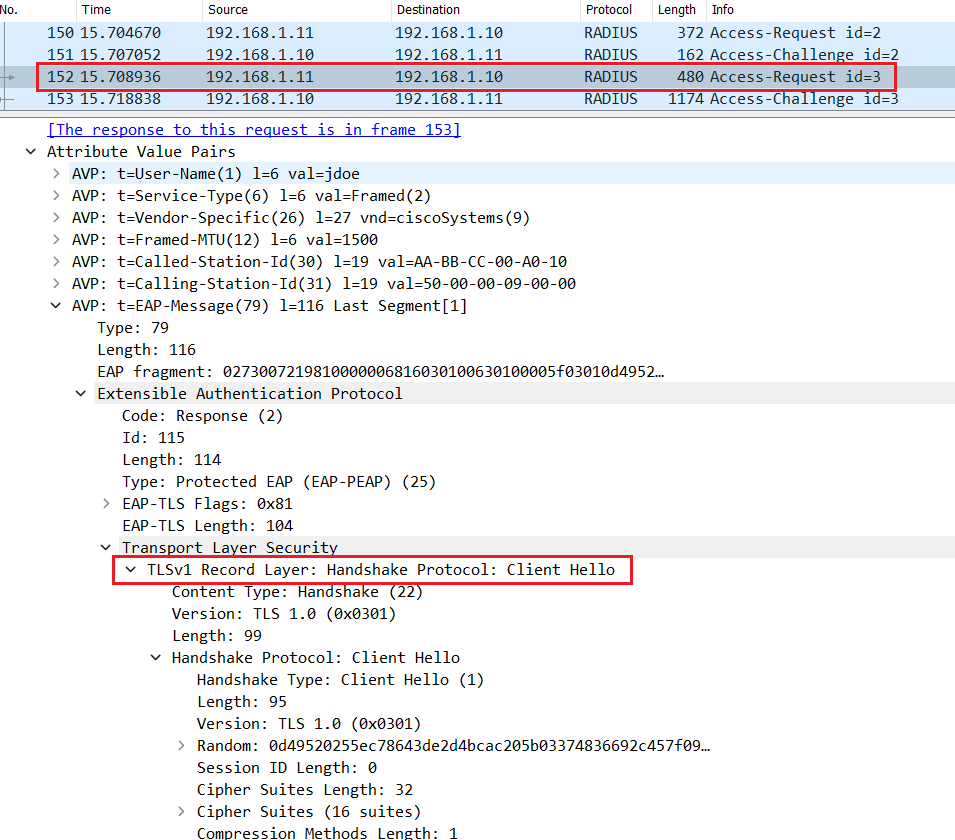
The switch relay the Client Hello inside the Radius Access-Request packet.
The server replies with a Server Hello in the Radius Access-Challenge packet with the chosen cipher and the server certificate of Cisco ISE.
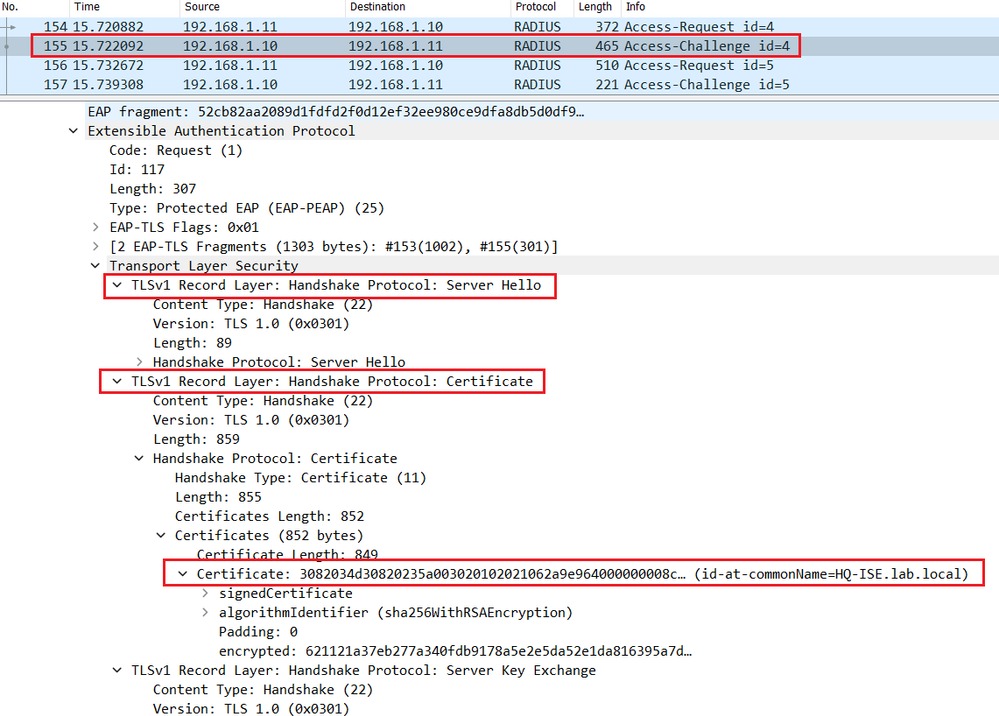
The switch relay the Server Hello in the EAP packet to the endpoint.
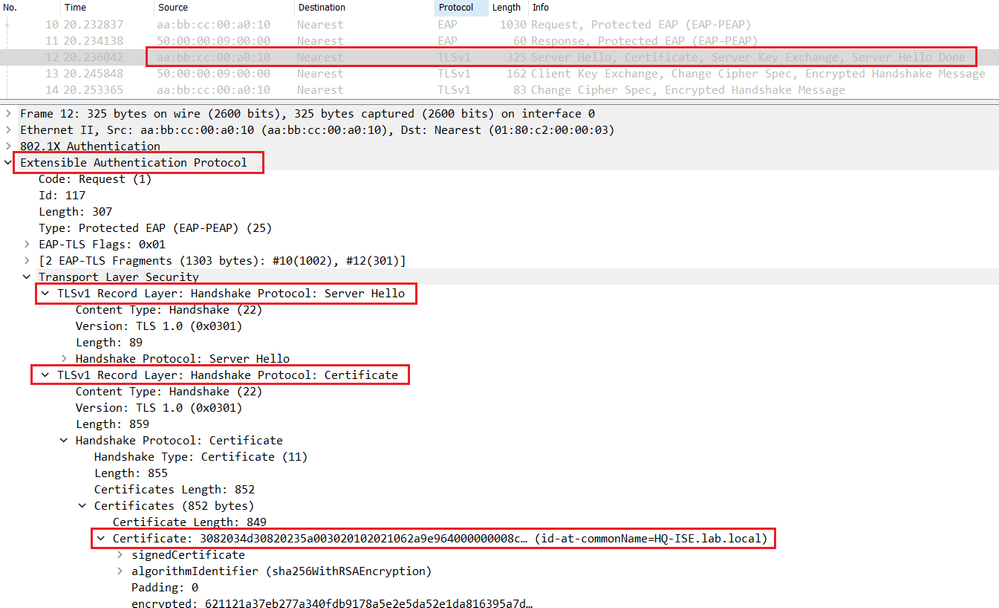
The endpoint validates the Server Certificate and sends a Client Key Exchange with the pre_master secret encrypted with the server's public key retrieved from the certificate.
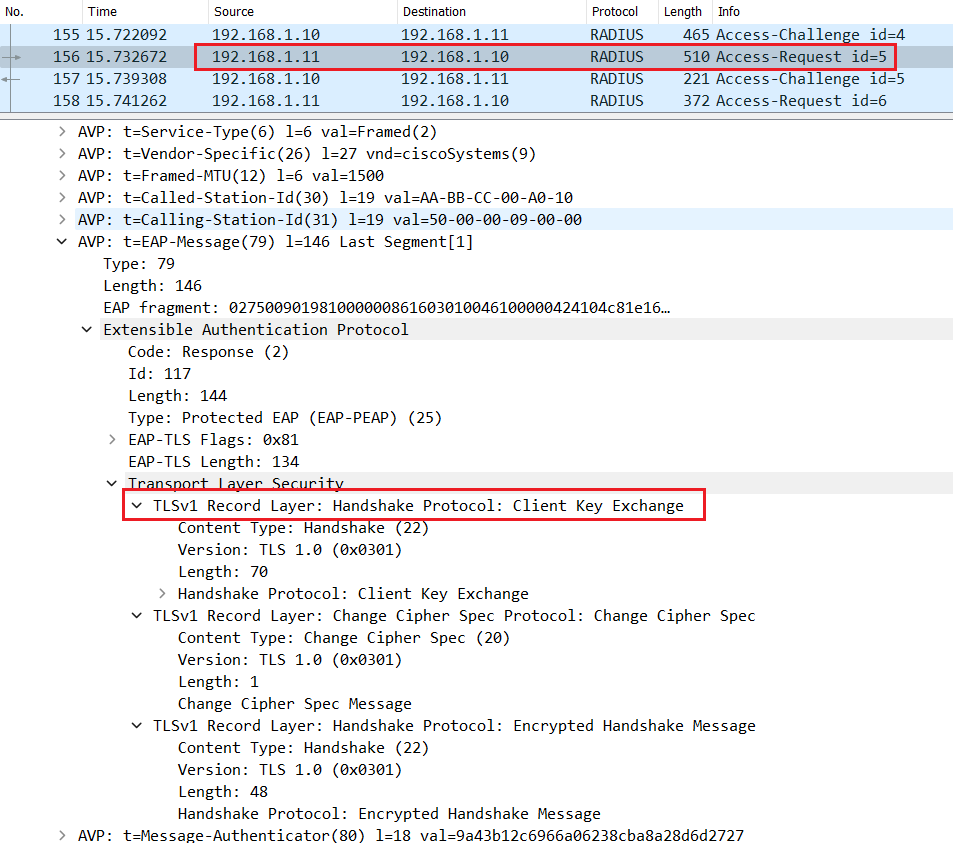
The switch encapsulates the EAP packet containing the Client key Exchange with Radius and sends a Radius Access-Request message.
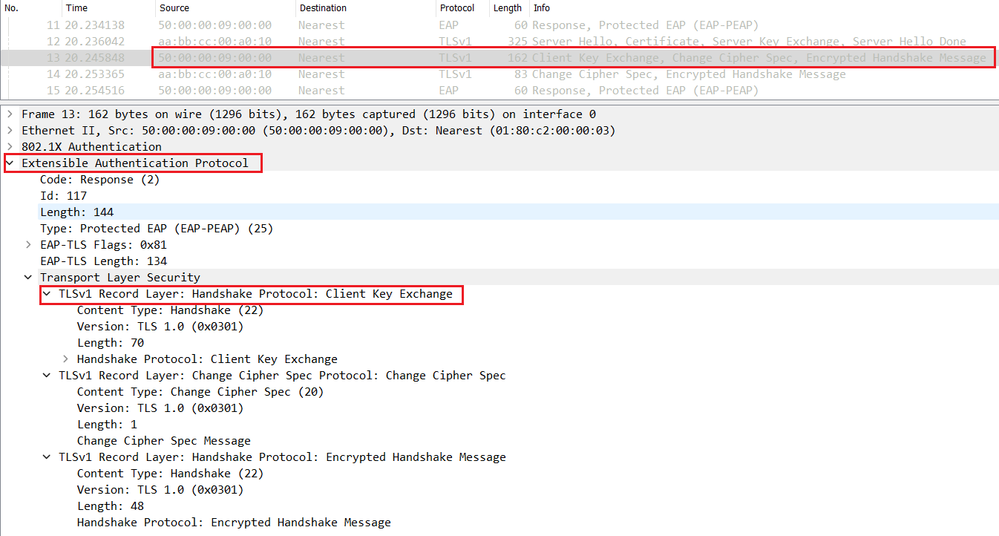
Cisco ISE decrypts the encrypted pre-master key using its own private key, and sends a Change Cipher Spec in the Radius Access-Challenge.
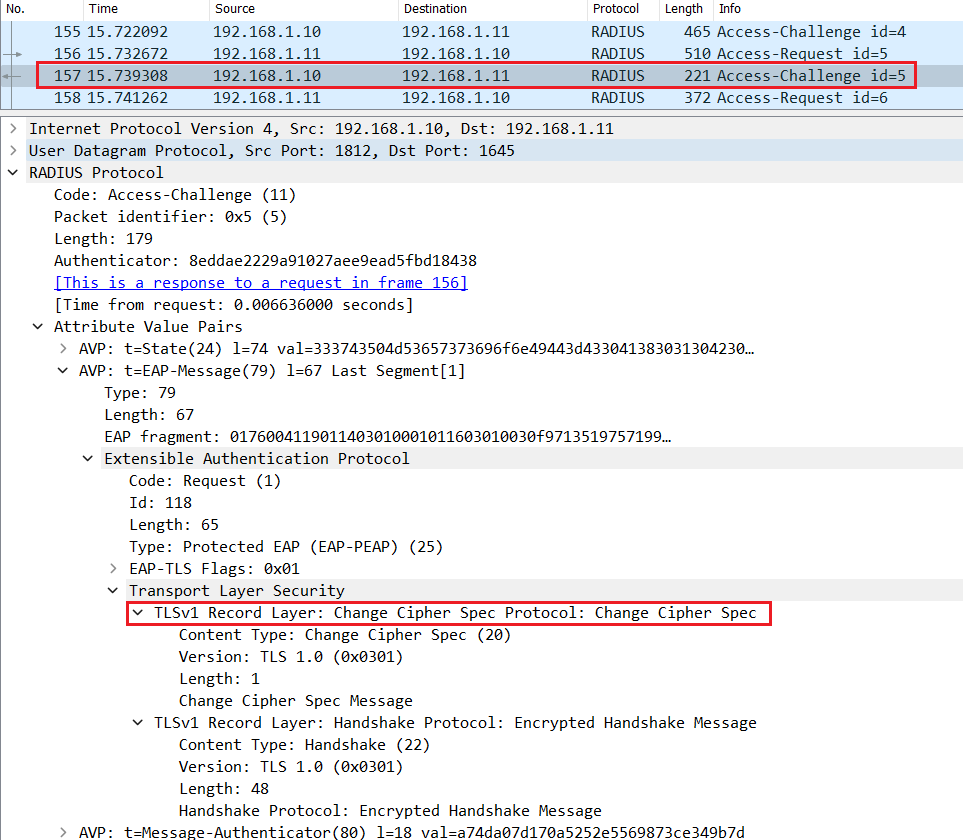
The switch relay an EAP packet containing the Change Cipher Spec to the endpoint.
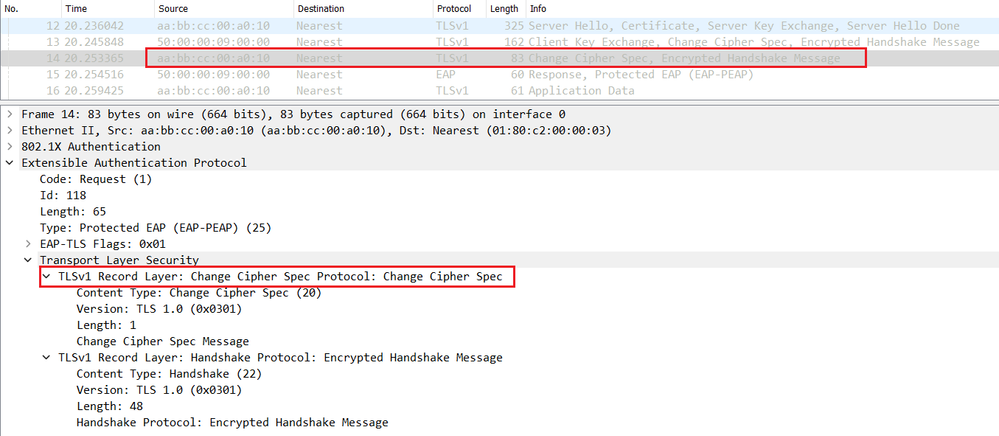
Now both Endpoint and Cisco ISE generate the session key that will be used to encrypt the phase 2 or the inner method MSCHAPv2 negociation and to securely authenticate the endpoint as show below.
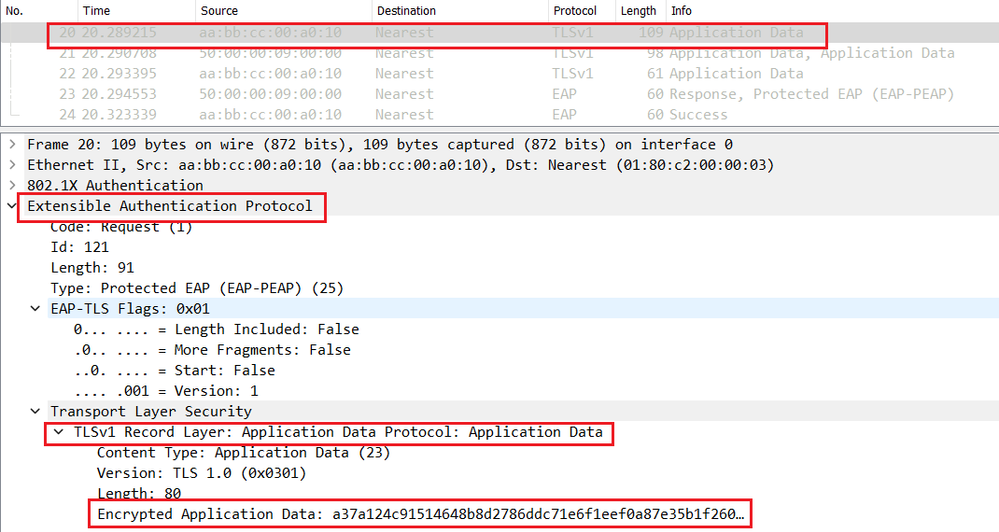
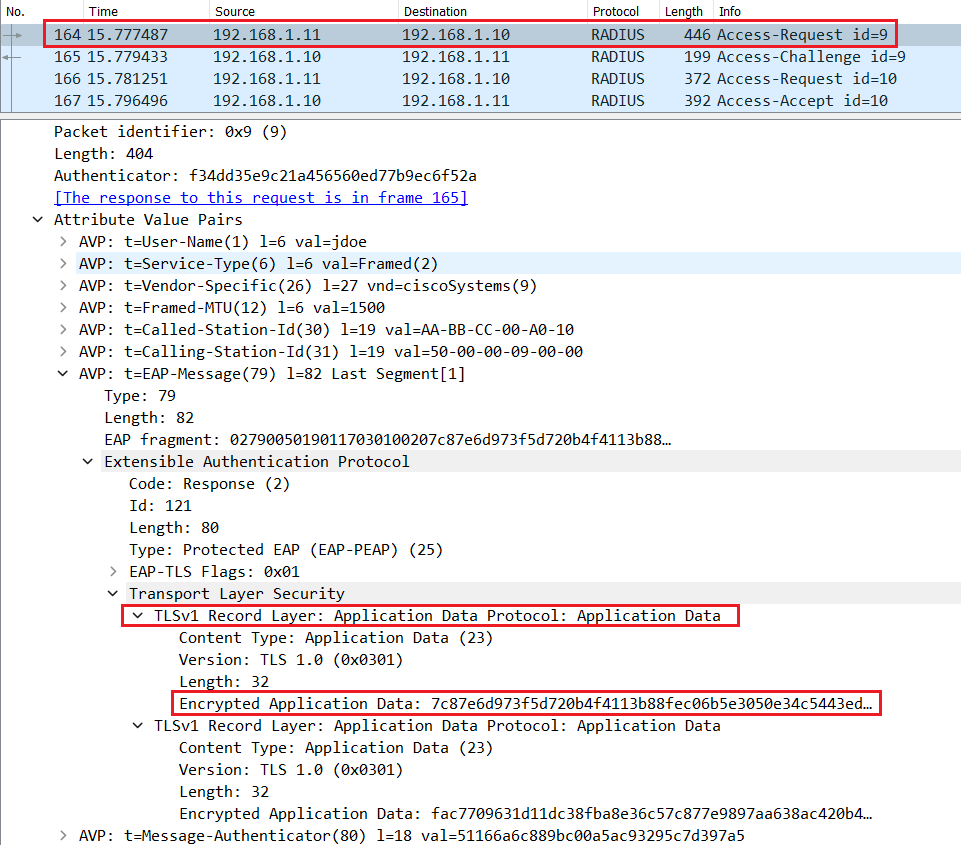
If the user enter a valid username and password, Cisco ISE will send a Radius Access-Accept message with EAP-Success in the L7 informations.
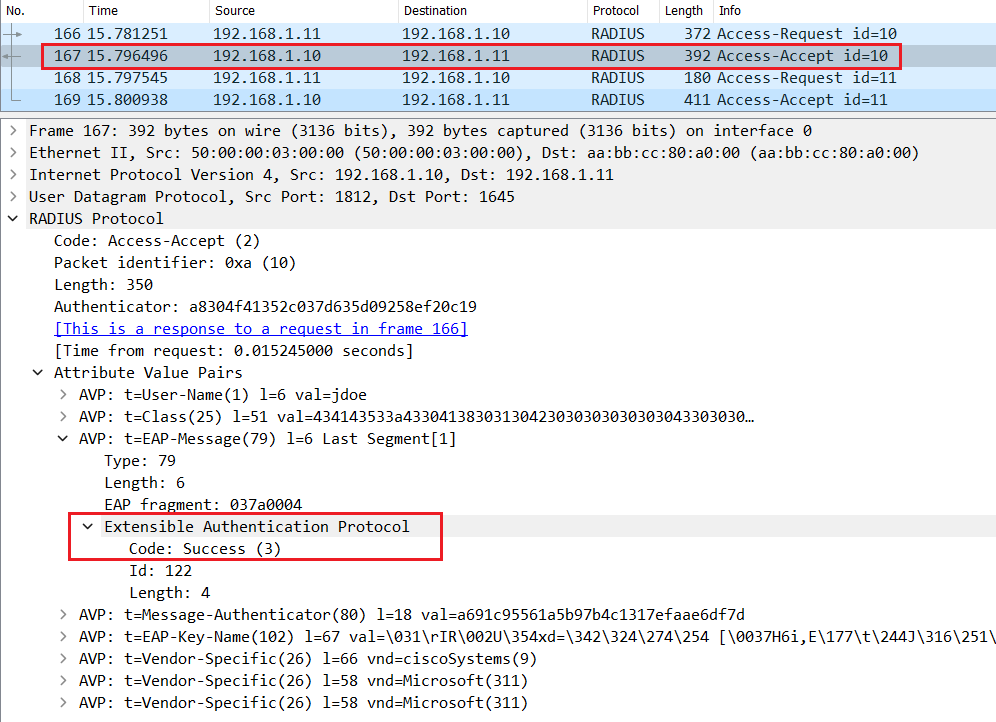
Finally the Switch sends an EAP message EAP-Success to the Endpoint.

