- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Knowledge Base
- CUCM Uploading CCMAdmin Web GUI Certificates
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-05-2009 11:48 AM - edited 03-12-2019 09:21 AM
1. Verify Hostname and Settings
Certificates are based on names. Make sure the names are correct before starting.
From SSH CLI
admin: show web-security
Subject: CN=CUCM7-PUB.bbbburns.lab, OU=TAC, O=Cisco, L=RTP, ST=North Carolina, C=US
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:CUCM7-PUB.bbbburns.lab, DNS:CUCM7-Pub
Use CLI to change these settings if desired
In the next example we move to BXB, and set an Alternate name of “ThePub” so we can type that into our browser
admin: set web-security TAC Cisco BXB Massachusetts US ThePub
After running "set web-security" Tomcat must be restarted for the new certificate to be used when accessing CCMAdmin and CCMUser.
admin: utils service restart Cisco Tomcat
2. Generate and Download CSR
OS Admin > Security > Certificate Management > tomcat.pem > Generate CSR
Download CSR (CUCM7-Pub.csr)
Note: Prior to CUCM 8.0(3), these Tomcat CSRs were generated with 1024 bit RSA keys. With the resolution of defect
CSCso62711 Cert Manager should generates Tomcat CSR using RSA 2048 instead of 1024
CUCM in versions 8.0(3) and later will generate a 2048 bit key / CSR for Tomcat. This defect currently only addresses Tomcat in 8.0(3). Other types of CSRs (like CallManager) will be addressed in future versions. Follow defect CSCtn01236 for 2048 bit updates.
3. Submit CSR to CA
Open the CSR file downloaded from the previous step (CUCM7-Pub.csr in this example) in Notepad and copy the entire contents including the ---BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST--- and ---END CERTIFICATE REQUEST-- lines.
If your CA is Windows 2k3
https://<CA Server Name: In my example JASBURNS-AD>/certsrv > Advanced Certificate Request
Paste the contents into this window to submit the request.
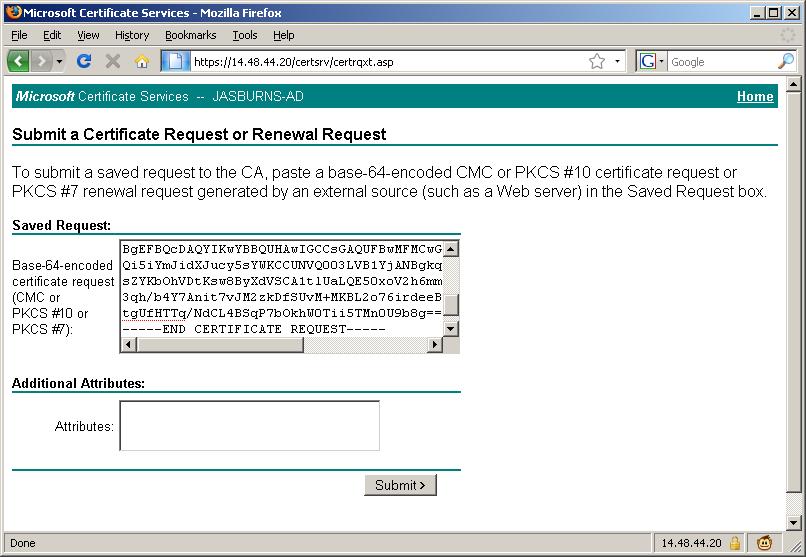
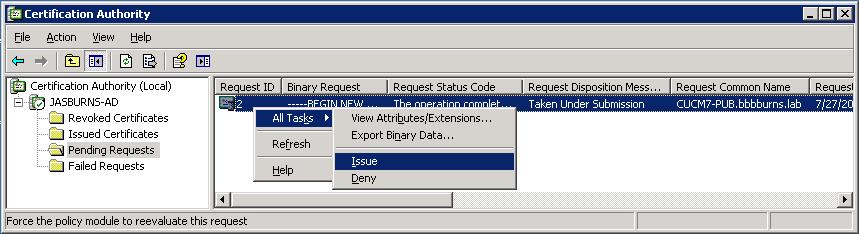
4. CA Approves CSR
This is where the magic happens.
The CA inspects the CSR and determines if the person submitting the CSR really owns CUCM7-PUB.bbbburns.lab
With Verisign or GoDaddy this step will require payment, and email or maybe even human verification
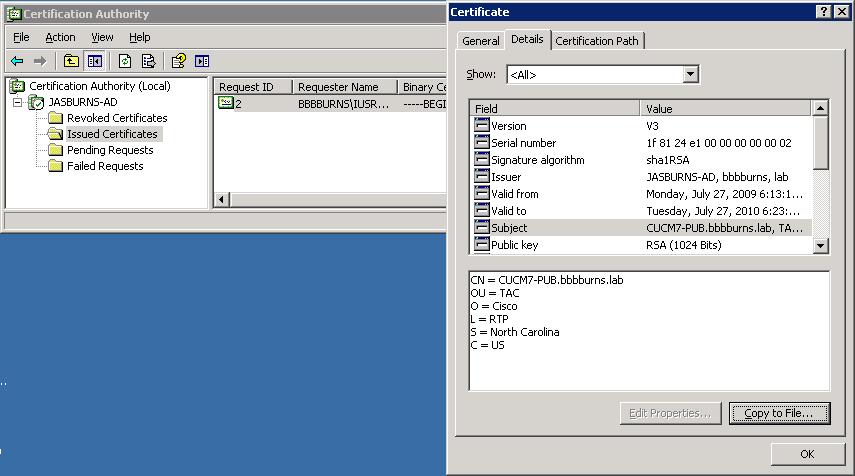
5. Server Admin Downloads Issued Cert
With Win2k3 go to CA MMC > Issued Certificates > Copy to file > Base-64 > (CUCM7-Pub.bbbburns.lab.cer)
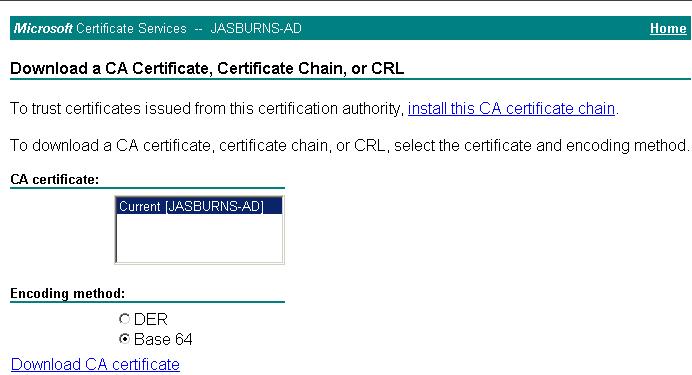
6. Server Admin downloads CA Cert
The Server Admin must build a complete chain of certs, so needs to download the root CA cert
https://<CA Server Name: In my example JASBURNS-AD>/certsrv > Download CA Cert > Base-64 > (jasburns-ad_PEM.cer)
7. Server Admin Uploads Root Certificate(s) as tomcat-trust
CUCM Server needs to have all certificates in the chain uploaded, starting at the top (root).
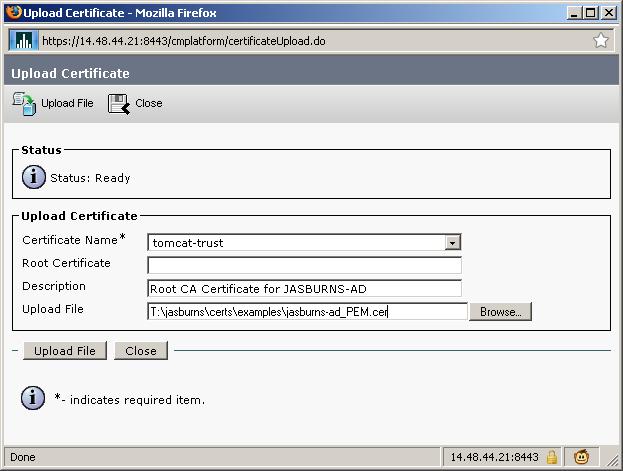
Note that the name of the file uploaded is jasburns-ad_PEM.cer. This is a Base64 encoded PEM file. Once it gets uploaded to CUCM though it will show up with filename JASBURNS-AD.pem. CUCM changes the name of the file to <SUBJECT CN>.pem.
7b. Uploading an intermediate certificate
This step is only necessary if the Certficate Authority (CA) has provided a signed certificate with multiple certificates in the certificate chain as shown.
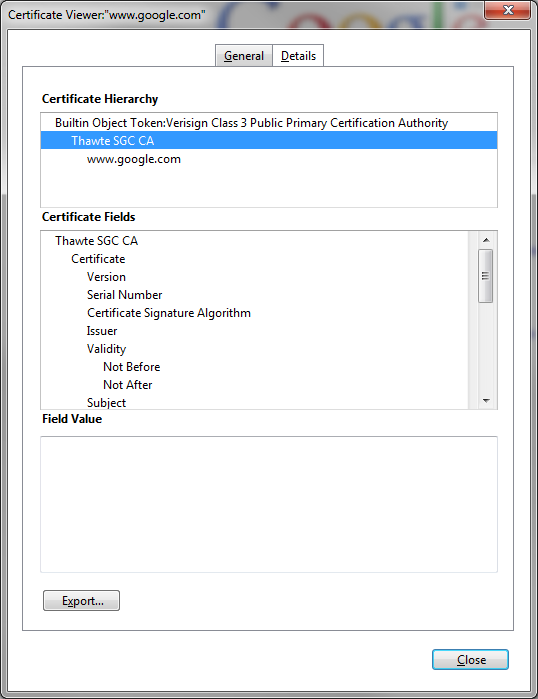
After uploading the root certificate in Step 7, export the intermedia certificate and upload it as a Tomcat-trust also while specifying the filename (minus the extension) of the root certificate in the "Root Certificate" field.
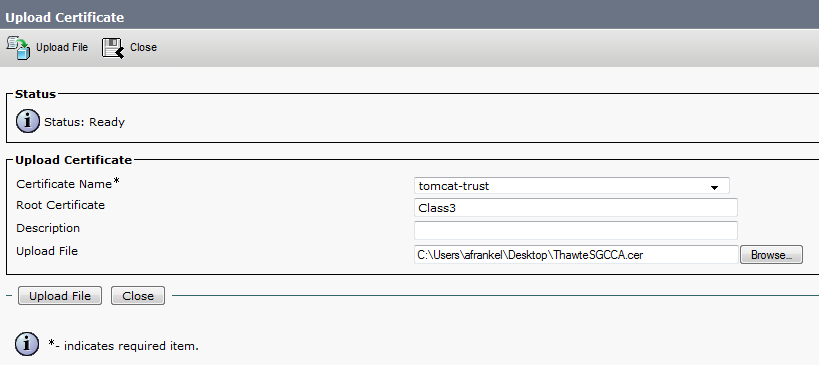
If there are more intermediate certificates in the chain, each one will need to be uploaded in order until finally uploading the signed certificate as shown in Step 8.
The purpose here is to build a chain of certificates. We upload the root certificate and leave the root cert field blank. When we upload the 1st intermediate certificate we put the file name of the root certificate in the root cert field. If there is 2nd intermediate, we put the name of the 1st intermediate in the root cert field. This builds the chain of trust that can be followed from the identity certificate to the root certificate.
8. Server Admin Uploads Identity Certificate as tomcat
This is the identity certificate issued by the CA.
Complete the cert chain by specifying .pem root cert. Note that the name below is JASBURNS-AD.pem. That's because I went to the OS Admin Certificate page to get the name of the newly uploaded tomcat-trust certificate from the last step. This is VERY important.
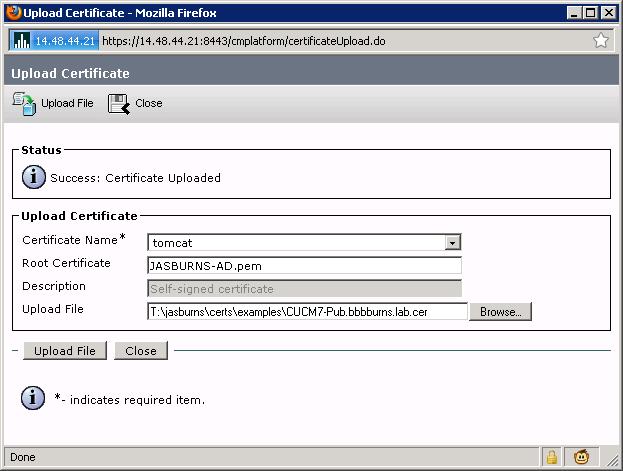
The root certificate you specify here could be the name of the root cert, or the name of some intermediate cert. The purpose is to find the certificate that signed the identity certificate, and use that certificate file name in this root cert field.
9. Restart Tomcat
This one is pretty simple. Just restart Tomcat from the SSH CLI
admin: utils service restart Cisco Tomcat
When Tomcat comes back up you can access the CCMAdmin or CCMUser GUI to verify your newly added certificates in use.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
As far as I can see I have followed this exact procedure on CUCM 7.1.3(b) but after restarting the Tomcat service the original self-signed cert is still in use. I can see the new cert and root cert in the list but it is just not in use.
Am I missing something, is there anything else I can check?
Jason
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
If you have modified any details using 'Set Web-security ..' make sure you regenerate tomcat certificate before generating CSR.
It can be done going to CLI
'set cert regen tomcat'
or GUI,
OS Admin > Security > Certificate Management > Generate New >Tomcat
Rest details remains same.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Good document, informative !
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Excellent document! It might be useful to summarize how to test the newly added CERT's. Typically its by browsing to the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) and not the ip address or hostname!
Also not sure if its worth mentioning that usually the chain of cert's from CA required will be in the DER encoded binary X.509 format.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Can CUCM support wildcard certificates using these same procedural steps?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
CUCM does not currently support wildcard certificates. There is an enhancement request opened for it,
CSCta14114.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
I following this link. https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-18689
I need to do for SIP TLS between CUCM and UM Exchange. what is diferent in the procedure?. If you know at leat one question please tell me any thing is help.
1) what is the service i need to restart?
2) in step 5 and 6 I dont know if is base 64 or DER?.
3) I think the step 7 we need to choose "certificate name = calmanger-trust"
4) I think the step 7 we need to choose "certificate name = calmanger"
thanks very much.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The procedure is very similar and uses the same basic concepts.
1. You need to restart the CallManager service after completing all of the steps.
2. Open the certificate file with notepad.exe. If you can read the "begin certificate" and "end certificate" lines you have a base64 PEM file. If the file is just binary special characters then you probably have a DER encoded file. Note that if you have a pkcs7 or pkcs12 file then you need to follow a different procedure to extract the individual certs from the file and save them as base64 PEM files. You can tell if you have the pkcs7 or 12 files because they will end with a file extension containing, 7, 12, of pfx.
3. Yes.
4. Correct.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
I'm tring to upload certificate to Unity Connection 8.6(2a)SU1
Tried to follow the steps above, problem is that there is no Roote Cetrificate field under Certificate management > Upload Certificate / Certificate chain??
Any idea?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Jason,
One of my client's CA root certitficate has expired, you can see the same in the screenshot.
I understand that we will have to regenrate the certitifcate and get it signed from CA and then upload it the CUCM box.
What I am trying to understand is what is the significance of these certificates and what will happen if I keep ignoring the expired certitifcate and do not regenrate it.
What impact does the exipred certitifcate has on producation envirenment?
Certificate was valid from: 8/10/2007 till 8/8/2012.
Please explain.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Nirmal,
Functionally there is no impact of this expired certificate. The session is still HTTPS / SSL encrypted. The only problem is that you will keep getting that warning, and might not notice if a REAL warning shows up about the site's authenticity.
Hope this helps!
-Jason
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Am I correct in saying that there is no impact to phones when changing certs?
Thank you
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
You can change the Tomcat certificate with no impact to the phones.
This gets a little more complicated if you're using CUCM 8.X and above. You can still change the Tomcat certificate with no problem, but you have to make sure you restart TVS and TFTP afterward because the new HTTPS and TVS services are going to rely on the Tomcat certificate when the phone goes to a secure service URL.
If you start talking about changing certs OTHER than Tomcat I'd recommend caution and searching for my other document on Security By Default.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Jason
As indicated by tdudas, there is no option to specify Root Certificate field in the Upload window.
Can we just upload the 3 certificates the same way, without specifying the root certificate? Or is the procedure different for CUCM 8.X? It's not explained in details in the OS Admin Guide.
You said that TFTP and TVS should be restarted as well for the Secure Service URL. I suppose that means that we have to add the hostnames/fqdn of external servers or load balancers which are used for CUCM services to the certificates?
Also, if the cluster is in secure mode, does this mean we have to update the CTL with the new tomcat certificates?
Thanks
Thijs
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi
CUCM 10
We are using 3rd party CA and we can only create 1 certificate per subject
I created CSR, generated a certificate and installed it for tomcat service as well as root cetificate for tomcat-trust. Everything working fine for that service.
I added root cetificate from our CA provider to Callmanager-trust
Can I somehow export existing certificate with private key from tomcat service and re-use it for CallManager service or any other service on the server?
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: